Coolant level
The coolant level should be checked at least once a week and before long trips. Check with a cold engine.
The fluid level must be between the marks "MIN" And "MAX" (pic. A:12) on the translucent wall of the expansion tank or inside the radiator filler neck.
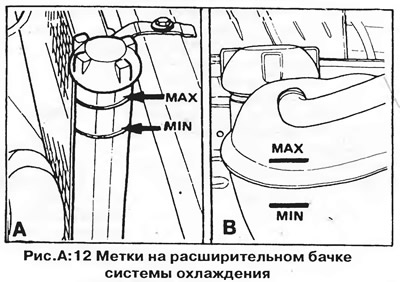
To add coolant, unscrew the expansion tank/radiator cap. When adding coolant, use a mixture of the same composition as the one in the cooling system. The proportions of the mixture of water and antifreeze are shown below.
NOTE: If it becomes necessary to add coolant frequently, carefully inspect the system for leaks. The coolant should be changed every two years.
Antifreeze
Since antifreeze has a lower freezing point and a higher boiling point than water, it is recommended to use it all the time to keep the engine from defrosting and from overheating. In addition, automotive antifreezes contain corrosion inhibitors that prevent internal corrosion of parts of the cooling system.
In the cold season, antifreeze must be poured into the system. The proportions of mixing antifreeze with water are indicated in the section "Technical data" and depend on climatic conditions and antifreeze manufacturer's recommendations. The total amount of antifreeze in the mixture should not be less than 30% by volume.
Before filling the system with antifreeze, carefully check the condition of the hoses, clamps and system connections. After filling the fluid, warm the engine up to operating temperature and check for leaks.
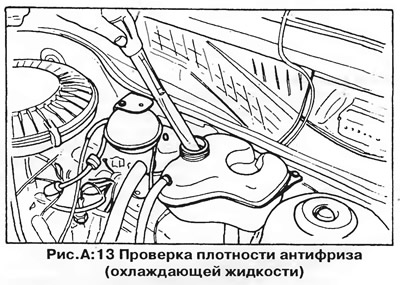
Measure the concentration of antifreeze with a special hydrometer (pic. A:13). At a concentration of antifreeze of 50%, its density is 1.073.
The coolant must be replaced with a system flush every two years, as long-term operation reduces the effectiveness of anti-corrosion additives.
NOTE: When sealants are used in the cooling system, the density of the antifreeze may change.
Checking the condition of the hoses
Periodically (especially before the onset of winter and filling the system with antifreeze) inspect the hoses and connections of the cooling system for timely detection of fluid leaks.
When inspecting hoses and connections, look for cracks, chafing, delamination of hoses, tears, or softening of the rubber. Replace damaged hoses.
Check the condition of the hose clamps. Tighten and replace clamps if necessary.

Visitor comments