
2. Unscrew and remove the bolt securing the selector shaft assembly (photo 6.19).

3. Unscrew the nut and remove the lever from the shaft, pay attention to that. that the installation of the lever on the shaft is possible only in one position (photo 6.20).

4. Remove the rubber cover of the selector shaft (photo 6.21).

5. Unscrew the cover protecting the selector shaft assembly (photo 6.22).

6. Set the gap in the gearbox with the selector shaft and in this position knock out the assembly in the direction of the larger hole (photo 6.23)

7. Unscrew the bolts and remove the rear cover of the gearbox (photos 6.24 and 6.25).


8. Remove the springy fuse of the pusher lever (photo 6.26).

9. Pull the clutch disengagement lever out of the housing (photo 6.27), while removing the clutch pusher lever (photo 6.28) and return spring (photo 6.29)



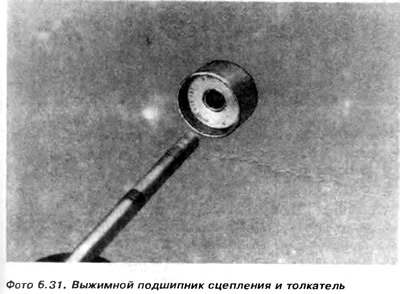
10. Remove the release bearing, clutch and pusher (photos 6.30 and 6.31).

11. Lift and remove the plugs, and then unscrew the three nuts securing the input shaft ball bearing (photo 6.32).

12. Unscrew and remove the bolt securing the reverse shaft (photo 6.33).

13. Lift and remove the plastic cap from the middle of the left drive flange. Bend the drive flange using a tensioner and remove the circlip and washer (photo 6.34). then remove the flange (photo 6.35).


It should be noted that the washer under the spring ring is placed with its concave side towards the drive flange.
Under the drive flange is a spring, a spring plate and a conical bronze ring. This ring is tapered towards the final drive gear.
14. Loosen the bolts connecting the main gearbox housing to the clutch housing, and then, using a tightener, pull the main housing off the bearing on the clutch shaft. Remove bearing spacer (if available), special bolts securing the bearing and remove the magnet from the clutch housing (photo 6.36).

15. Remove the slider and fork assembly (pic. 6.9).
16. To take out a gear wheel of a backing together with a gear wheel.
17. Remove the 4th gear retaining ring on the output shaft, and then remove the 4th gear using a puller if necessary.
18. Only after removing the 4th gear from the output shaft can the clutch shaft assembly be removed as a whole -!!!!
19. Remove the slider from the clutch housing and remove the fork assembly 17 to the side (pic. 6.9).
20. Remove the input shaft assembly from the clutch housing
21. Remove the 3rd gear protective spring ring from the output shaft, and then remove; 3rd and 2nd gears, second speed synchronizer ring, needle bearing
Using a tensioner installed under the first speed gear, remove the following items: the inner track of the needle bearing of the second speed six, the synchronizer hub with the reverse gear, which is both a movable clutch of the 1st and 2nd speeds, called the mobile gear, the first speed synchronizer ring, the gear first speed with needle bearing (you will need a puller with long legs).
22. Remove the bell-shaped distance washer 1, which rests on the disc that secures the bearing. The washer faces the concave side towards the tapered bearing.
23. Unscrew the bolts 25 and remove the disc that secures the bearing and remove the output shaft from the clutch housing.
24. Remove the remaining drive flange, then remove the differential mechanism assembly. It is better to entrust the repair of the differential mechanism to specialized workshops and not to do it on your own.
25. To repair the clutch housing, no special tool is needed, and the actions are similar to those described in paragraph 4. Sleeve 6 is pressed into the clutch housing (pic. 6.10). It can be lifted with a screwdriver, however, care must be taken not to damage the housing. After removal, the sleeve must be replaced with a new one. The new bushing is pressed into place using a suitable tubular punch.
26. If necessary, replace the tapered bearings of the output shaft or differential gear, note that the small and large bearings fix the position of the output shaft in relation to the final drive gear. We make the appropriate installation using a spacer, which is selected from 16 available washers of different thicknesses.
The washer is inserted between the outer race of the smaller tapered bearing and the clutch housing. If at least one bearing is defective, both must be replaced. During replacement, old bearings break. New bearings are pressed in and a suitable spacer must be fitted under the smaller bearing.
27. This operation is quite complicated and requires measuring the longitudinal clearance of the output shaft using a clock gauge, as well as correctly determining the traces of the operation of the teeth of gears with oblique teeth. Tapered bearings must be prestressed. Evaluation of the correct prestressing is made by measuring the torque required for a day of rotation of the output shaft. The greater the prestressing, the greater the torque for rotation.
Attention: It must be borne in mind that the spacer of the input shaft and the longitudinal clearance measured on the spring ring that secures the 3rd gear on the output shaft are mutually dependent. This means that a new spacer and circlip need to be installed.
There are 6 different spring rings, differing in thickness. In the absence of sufficient experience and the appropriate tool, the bearings should be replaced by a specialized gearbox repair shop.
28. It must be remembered that the input shaft ball bearing must be pressed into the gearbox housing with a wider ring of the inner race in the direction of the 4th speed gear. If a spacer was installed, it must be placed in the housing before the bearing is pressed into the housing. Then it is necessary to insert the bolts securing the bearing, and tighten the nuts
29. The input and output shaft assemblies can be repaired as described in the next paragraph.
30. Inspection and maintenance of the differential mechanism is described in paragraph 7.
However, the following differences should be noted. concerning gearbox 020.
A) When determining the size of the distance washer, we accept. that the thickness of the washer is A + 0.40 mm.
b) We insert a spacer 1 mm thick into the gearbox clutch housing, and remote adjusting washers into the main gearbox housing.
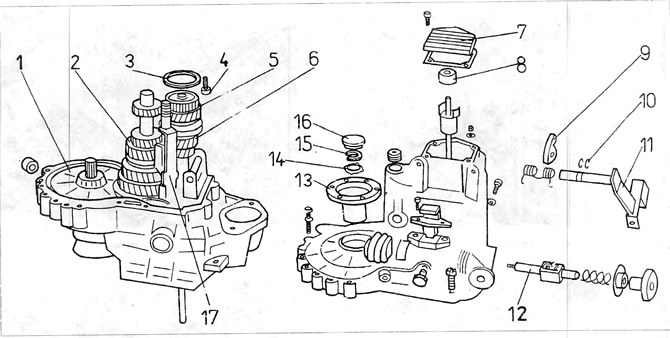
Pic. 6.9. Gearbox 020, 4-speed
1 - a large gear wheel of the main gear; 2 - output shaft, 3 - distance washer between the bearing and the box body; 4 special bolt securing the input shaft bearing; 5 - bearing; 6 - input roller; 7 - back cover; 8 - clutch release bearing; 9 - clutch pusher lever; 10 - springy rings; 11 - switching off lever; 12 - shaft; 13 - drive flange; 14 - concave washer; 15 - clamping ring; 10 - plastic plug; 17 - knot forks with a slider.

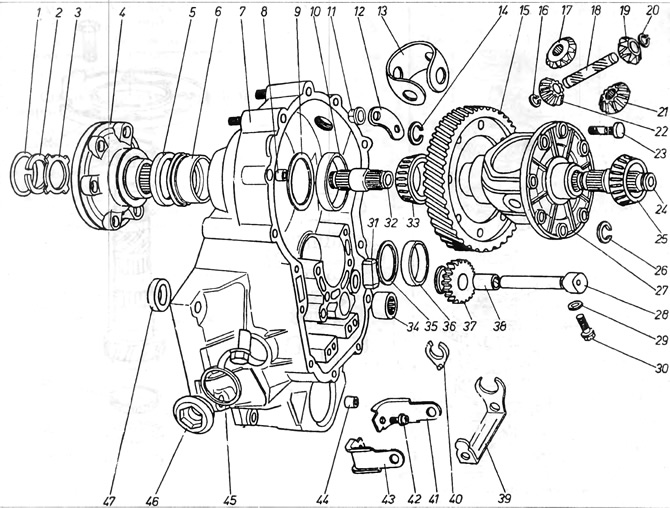
Pic. 6.10. Differential mechanism 020
1 - plastic plug; 2 - spring ring; 3 - concave washer; 4 - drive flange; 5 - flange seal; 6 - seal bushing; 7 - clutch housing; 8 - fixing pin; 9 - washer; 10 - bearing track; 11 - nut; 12 - washer; 13 - clip; 14 - spring ring; 15 - a large gear of the main gear; 16 - spring ring; 17 - satellite; 18 - roller satellites; 19 - satellite; 20 - spring ring; 21 - satellite; 22 - satellite; 23 - a bolt that secures the large final drive gear to the basket of the differential mechanism; 24 - short axle shaft; 25 - conical bearing; 26 - spring ring; 27 - a basket of satellites; 28 - reverse gear roller; 29 - washer; 30 - bolt; fixing roller reverse; 31 - magnet; 32 - short axle shaft; 33 - conical bearing; 34 - needle bearing of the input shaft; 35 - remote washer; 36 track of the lower conical bearing; 37 - reverse gear; 38 - reverse gear bushing; 39 - reverse gear forks; 40- plastic insert for forks; 41 - support stacking forks; 42 - fixing bolt; 43 - support stacking forks; 44 - fixing peg; 45, 46 - TDC hole plug; 47 - puck.
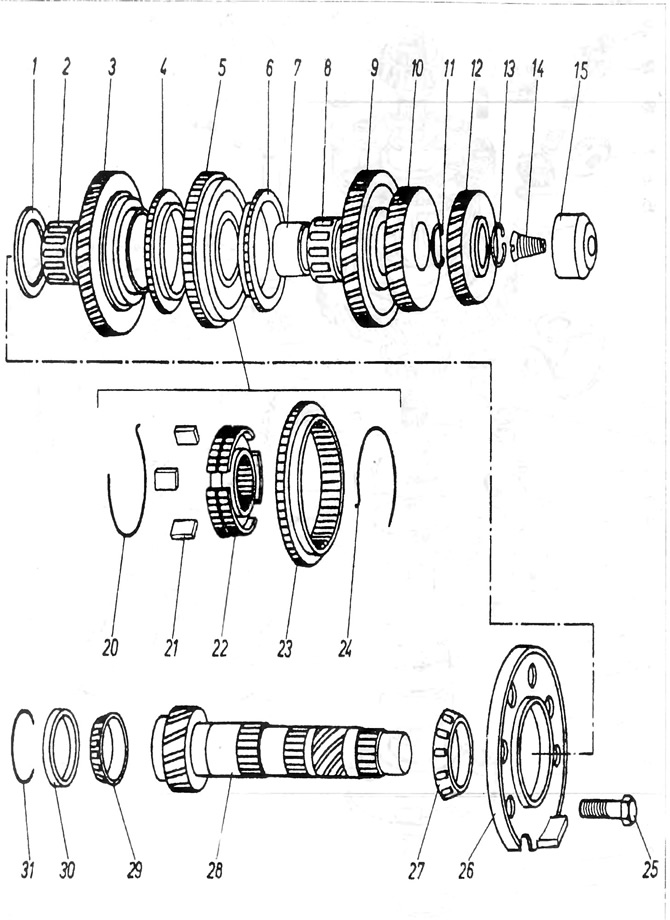
Pic. 6.11. Output roller box 020, 4-speed
1 - concave washer; 2 - 1st gear needle bearing; 3 - 1st gear gear; 4 - synchronizer ring; 5 - synchronizer unit of the 1st and 2nd speeds; 6 - synchronizer ring; 7 - track of a needle bearing; 8 - needle bearing; 9 - gear wheel of the 2nd speed; 10 - 3rd gear gear; 11 - spring ring; 12 - gear wheel of the 4th speed; 13 - spring ring; 14 - screw securing the needle bearing in the box body; 15 - needle bearing; 20 - ring supporting crackers 21 - crackers; 22 - synchronizer hub; 23 - movable gear with reverse gear; 24 - a ring supporting crackers; 25 - bolt securing the bearing disk; 26 - bearing disk; 27 - conical bearing; 28 - output shaft; 29 - lower conical bearing; 30 - track of the lower bearing; 31 spacer for the lower bearing race.
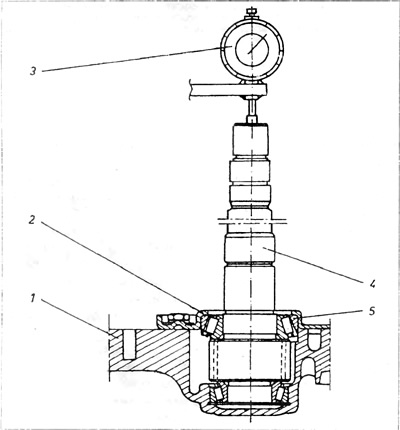
Pic. 6.12. Measuring the longitudinal clearance of the output shaft
1 - clutch housing; 2 - bearing disc; 3 - hour sensor; 4 - output roller; 5 - upper conical bearing.

Visitor comments