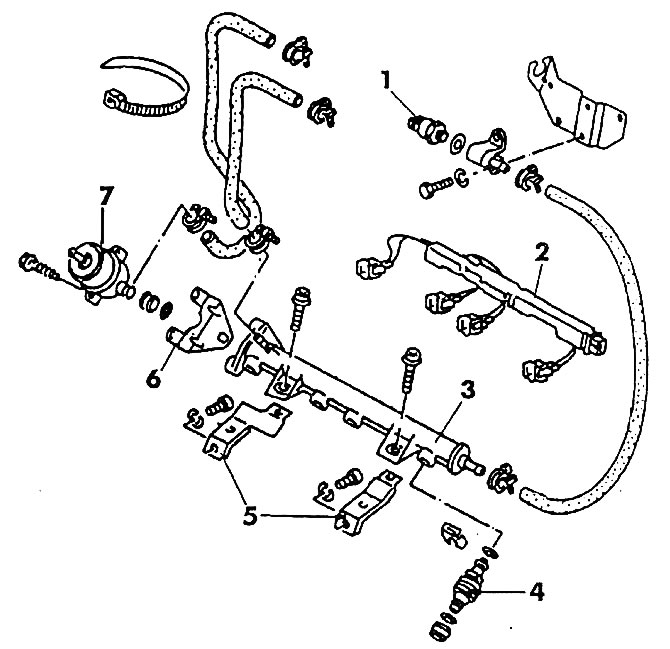
Pic. 176. Components and parts of the Digifant fuel injection system: 1 - thermal switch (keeps the fan running after the engine is turned off); 2 - wires and plugs of injectors; 3 - fuel rail; 4 - nozzle; 5 - holders; 6 - support; 7 - fuel pressure regulator
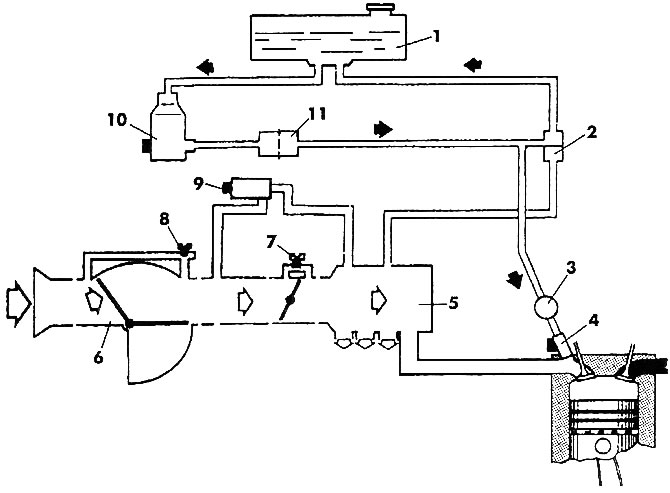
Pic. 177. Elements of the Digifant injection system (electronics not shown): 1 - fuel tank; 2 - pressure regulator; 3 - ramp; 4 - nozzle; 5 - intake manifold; 6 - flow meter; 7 - screw for adjusting the idle speed; 8 - screw for adjusting the CO content; 9 - idle speed stabilization valve; 10 - fuel pump; 11 - fuel filter
The presence of an electronic control system ensures operation with an adjustable catalyst. Many control and work operations apply both to the Digiapt fuel injection system and to the K- and KE-Jetgopis systems. In the following description of the operating steps, each time it is indicated which system this description refers to.
The Digifant fuel injection system has elements for idling speed stabilization and forced idling shutdown. The fuel is pumped out of the fuel tank by the supply fuel pump located in the tank and fed into the pump's fuel accumulator. The main fuel pump delivers fuel through the fuel filter to the fuel rail. A ramp connected to the pressure regulator ensures constant pressure. It also has the function of fuel accumulation. From the rail, fuel enters the corresponding engine cylinders through electromagnetic nozzles. They carry out periodic, that is, pulsed, injection of fuel in the intake pipe directly onto the intake valves. The amount of injected fuel is controlled by the duration of the injection.
The duration of the injection depends on the following quantities: intake air quantity, engine temperature, engine speed, intake air temperature, throttle position, oxygen content in the exhaust gases.
The Digifant system combines ignition and fuel injection control functions in one control unit. The ignition system here is a transistorized ignition system with a Hall sensor and an electronic unit that regulates the ignition timing. It controls the ignition timing according to a given field of ignition parameters. Additionally, the knock sensor also influences the formation of the ignition moment. The system does not require maintenance.

Visitor comments