Golf 1 (1974-1984, diesel)
Golf 1 (1974-1984, petrol)
Golf 2 (1984-1993, petrol)
Golf 2 (1984-1993)
Golf 3 (1991-1997)
Golf 4 (1997-2004)
Golf 5 (2003-2008)
Diesel engine repair car Volkswagen Golf 2
Description of diesel and turbodiesel engines
Brief characteristics of diesel and turbo diesel engines are given in tab. 1 . GOLF II and Jetta II vehicles are equipped with four-stroke in-line diesel engines with prechamber...
Brief characteristics of diesel and turbo diesel engines are given in tab. 1 . GOLF II and Jetta II vehicles are equipped with four-stroke in-line diesel engines with prechamber...
Removal and installation of the engine
The dismantling of diesel engines is carried out in the same way as the removal of gasoline engines, the only differences are the following operations. Additionally, it is...
The dismantling of diesel engines is carried out in the same way as the removal of gasoline engines, the only differences are the following operations. Additionally, it is...
Engine disassembly
Disassemble the engine in the following order: Remove the vacuum pump, exhaust manifold, coolant pump and other accessories from the engine. Unscrew the four bolts securing the...
Disassemble the engine in the following order: Remove the vacuum pump, exhaust manifold, coolant pump and other accessories from the engine. Unscrew the four bolts securing the...
Engine Assembly
The engine is assembled in the reverse order. A more detailed description of the individual operations will be given in the following sections. Following are a few guidelines to...
The engine is assembled in the reverse order. A more detailed description of the individual operations will be given in the following sections. Following are a few guidelines to...
Cylinder head
Some design features of the valve mechanism will be described below. It is necessary to carefully read them before proceeding with any care for the repair of the cylinder head....
Some design features of the valve mechanism will be described below. It is necessary to carefully read them before proceeding with any care for the repair of the cylinder head....
Dismantling the cylinder head from the engine installed on the car
To remove the head of the block, it is not necessary to remove the engine from the car. If the engine has already been removed, the description of the first operations can be...
To remove the head of the block, it is not necessary to remove the engine from the car. If the engine has already been removed, the description of the first operations can be...
Dismantling of a head of the block of cylinders
All components and parts of the valve mechanism that will not be replaced must be installed in their original places. In order not to accidentally confuse them, it is necessary to...
All components and parts of the valve mechanism that will not be replaced must be installed in their original places. In order not to accidentally confuse them, it is necessary to...
Checking valve springs
It should be remembered that valve springs from engines with hydraulic tappets cannot be used in other engines, as they are shorter. To distinguish them, they are marked on the...
It should be remembered that valve springs from engines with hydraulic tappets cannot be used in other engines, as they are shorter. To distinguish them, they are marked on the...
Checking the valve guides
Clean the bushings and valve stems with a rag soaked in gasoline. Insert the rods into the corresponding bushings. On the mating plane of the block head, fix the indicator holder...
Clean the bushings and valve stems with a rag soaked in gasoline. Insert the rods into the corresponding bushings. On the mating plane of the block head, fix the indicator holder...
Checking valve seats
Processing of valve seats is carried out according to fig. 189. In the case of an engine with hydraulic pushers, you should read the instructions below. It is necessary that after...
Processing of valve seats is carried out according to fig. 189. In the case of an engine with hydraulic pushers, you should read the instructions below. It is necessary that after...
Checking valves
Diesel engines equipped with hardened valves (pic. 190). They can be recognized by the three grooves at the end of the rod. The design of crackers has also been changed (they have...
Diesel engines equipped with hardened valves (pic. 190). They can be recognized by the three grooves at the end of the rod. The design of crackers has also been changed (they have...
Checking the cylinder head
Thoroughly clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and engine block, and then check for warping of the mating surfaces of the cylinder head. Checking is carried out using a...
Thoroughly clean the mating surfaces of the cylinder head and engine block, and then check for warping of the mating surfaces of the cylinder head. Checking is carried out using a...
Checking the camshaft (engine with hydraulic pushers)
Engines with hydraulic valve lifters are equipped with a camshaft design that is different from the shafts designed to work with conventional tappets. This shaft has nitrided cam...
Engines with hydraulic valve lifters are equipped with a camshaft design that is different from the shafts designed to work with conventional tappets. This shaft has nitrided cam...
Checking hydraulic valve lifters
Hydraulic valve lifters have been fitted to engines since 1986. Improper maintenance of hydraulic tappets can lead to damage to engine parts: Therefore, after removing the...
Hydraulic valve lifters have been fitted to engines since 1986. Improper maintenance of hydraulic tappets can lead to damage to engine parts: Therefore, after removing the...
Cylinder head assembly
The block head is assembled in the reverse order of its disassembly. When assembling, follow these guidelines: Lubricate the valve stems well with engine oil and insert them into...
The block head is assembled in the reverse order of its disassembly. When assembling, follow these guidelines: Lubricate the valve stems well with engine oil and insert them into...
Installing the cylinder head
When ordering a head gasket, you must specify the correct engine identification data to obtain a gasket designed specifically for a diesel engine or a turbocharged diesel engine....
When ordering a head gasket, you must specify the correct engine identification data to obtain a gasket designed specifically for a diesel engine or a turbocharged diesel engine....
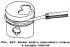
Pistons and connecting rods — design description
The details of the connecting rod and piston group are shown in fig. 199. To remove the pistons, the engine must be removed from the vehicle and the block head separated from the...
The details of the connecting rod and piston group are shown in fig. 199. To remove the pistons, the engine must be removed from the vehicle and the block head separated from the...
Extraction of parts of the connecting rod and piston group from the cylinder block
Pistons with connecting rods are removed from the cylinders upwards after removing the connecting rod bearing caps and liners. Before proceeding with these operations, you should...
Pistons with connecting rods are removed from the cylinders upwards after removing the connecting rod bearing caps and liners. Before proceeding with these operations, you should...
Checking the details of the connecting rod and piston group
All parts of the connecting rod and piston group are subject to inspection and, if they have deep scratches or signs of wear, must be replaced. Measure a backlash between piston...
All parts of the connecting rod and piston group are subject to inspection and, if they have deep scratches or signs of wear, must be replaced. Measure a backlash between piston...
Assembling the connecting rod and piston group
Heat pistons to 60°C (putting them in hot water), prepare a rod of equal or slightly smaller diameter than the diameter of the piston pin. Insert the piston pin by hand into the...
Heat pistons to 60°C (putting them in hot water), prepare a rod of equal or slightly smaller diameter than the diameter of the piston pin. Insert the piston pin by hand into the...
Installing the connecting rod and piston group
If the oil jets used to cool the pistons have been removed from a turbocharged engine, they must be reinstalled (pic. 206). Tighten the injector mounting bolts to 10 Nm. Copiously...
If the oil jets used to cool the pistons have been removed from a turbocharged engine, they must be reinstalled (pic. 206). Tighten the injector mounting bolts to 10 Nm. Copiously...
Measuring the end play of the crankshaft
Before removing the crankshaft, which can only happen on an engine removed from the car, it is necessary to measure its axial play in order to find out if it will be necessary to...
Before removing the crankshaft, which can only happen on an engine removed from the car, it is necessary to measure its axial play in order to find out if it will be necessary to...
Removing the crankshaft
Remove the engine from the car. Holding the flywheel ring gear with a screwdriver, remove the bolts. Usually, these bolts can be loosened with an ordinary wrench without locking...
Remove the engine from the car. Holding the flywheel ring gear with a screwdriver, remove the bolts. Usually, these bolts can be loosened with an ordinary wrench without locking...
Replacing the crankshaft seals
The front and rear oil seals must be replaced each time the crankshaft is removed from the cylinder block. Their installation requires a special tool and great care. Both oil...
The front and rear oil seals must be replaced each time the crankshaft is removed from the cylinder block. Their installation requires a special tool and great care. Both oil...
Checking the crankshaft
Carefully inspect the crankshaft for signs of damage, and then measure the diameters of the main and connecting rod journals. The necks have three repair sizes, which increases...
Carefully inspect the crankshaft for signs of damage, and then measure the diameters of the main and connecting rod journals. The necks have three repair sizes, which increases...
Installing the crankshaft
Wipe the nests of the main bearings in the engine block. Liners with oil groove 6 ( see fig. 183 ) insert into the nests so that the protrusion falls into the recess. Lubricate...
Wipe the nests of the main bearings in the engine block. Liners with oil groove 6 ( see fig. 183 ) insert into the nests so that the protrusion falls into the recess. Lubricate...
Cylinder block — check
To determine the degree of wear of the cylinder mirror, a caliper is required ( see fig. 71 ). Diameter measurements are made in two planes and in three sections along the height...
To determine the degree of wear of the cylinder mirror, a caliper is required ( see fig. 71 ). Diameter measurements are made in two planes and in three sections along the height...
Flywheel — replacement
Flywheel 10 (see fig. 209) A diesel engine differs from a gasoline engine flywheel in that it is not attached directly to the crankshaft, but by means of a clutch pressure plate....
Flywheel 10 (see fig. 209) A diesel engine differs from a gasoline engine flywheel in that it is not attached directly to the crankshaft, but by means of a clutch pressure plate....
Replacing the intermediate shaft
Replacement of an intermediate shaft is made only on the engine removed from the car. The shaft mounting method is shown in fig. 211. To remove the shaft, first remove the high...
Replacement of an intermediate shaft is made only on the engine removed from the car. The shaft mounting method is shown in fig. 211. To remove the shaft, first remove the high...
Automatic transmission drive
.The automatic transmission is connected to the crankshaft by a drive plate fixed with six bolts (pic. 212). The reinforcing ring has a chamfer on the outer edge, which must face...
.The automatic transmission is connected to the crankshaft by a drive plate fixed with six bolts (pic. 212). The reinforcing ring has a chamfer on the outer edge, which must face...
Gas distribution mechanism — design description
The scheme of the gas distribution mechanism is shown in fig. 214 (execution before January 1984). Until this time, the toothed belt was completely closed. The engine has...
The scheme of the gas distribution mechanism is shown in fig. 214 (execution before January 1984). Until this time, the toothed belt was completely closed. The engine has...
Timing Belt Banners
.The toothed belt can be replaced on an engine installed in a car, for which: Remove the toothed belt guard or guards. Loosen the alternator mountings by moving it to the center,...
.The toothed belt can be replaced on an engine installed in a car, for which: Remove the toothed belt guard or guards. Loosen the alternator mountings by moving it to the center,...
Camshaft Replacement
To dismantle the camshaft, do the following: Remove the cover (casings) toothed belt. Remove the valve cover. Turn the flywheel so that the piston of the 1st cylinder is at TDC,...
To dismantle the camshaft, do the following: Remove the cover (casings) toothed belt. Remove the valve cover. Turn the flywheel so that the piston of the 1st cylinder is at TDC,...
Camshaft oil seal replacement
The camshaft seal can be replaced without removing the engine from the vehicle. The oil seal is behind the camshaft sprocket. In order not to damage the surface of the block head...
The camshaft seal can be replaced without removing the engine from the vehicle. The oil seal is behind the camshaft sprocket. In order not to damage the surface of the block head...
Valve clearance adjustment
In engines that do not have hydraulic tappets, it is required to periodically check and adjust the valve clearance as necessary. This gap is measured with a feeler gauge between...
In engines that do not have hydraulic tappets, it is required to periodically check and adjust the valve clearance as necessary. This gap is measured with a feeler gauge between...
Maintenance of diesel and gasoline engines
Visual inspection An oil-splattered engine with high fuel consumption is checked for oil leakage. The following places and zones are checked: Open the oil filler cap and check the...
Visual inspection An oil-splattered engine with high fuel consumption is checked for oil leakage. The following places and zones are checked: Open the oil filler cap and check the...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections from other manuals for VW cars:
Power unit: Engines 4-cylinder FZ Volkswagen Passat B2 (1981-1988)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.4 and 1.6 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Petrol engine 1.4 CAVA Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Power unit: Engines 4-cylinder FZ Volkswagen Passat B2 (1981-1988)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.4 and 1.6 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Petrol engine 1.4 CAVA Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Golf 5
Golf 4
Golf 3
Golf 2
Golf 2 (petrol)
Golf 1 (petrol)
Golf 1 (diesel)
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling and ventilation system
- Fuel system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Interior (internal elements)
- Exterior (external elements)
- Doors and covers
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Washers and wipers
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Weekly checks
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines
- Diesel engines
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (petrol)
- Control system (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Ventilation and heating
- Car doors and sunroof
- Washers and glass cleaners
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- Petrol engine
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engine
- Engine repair
- Diesel injection system
- Pre-glow system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Gearbox and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Wheels and suspension
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to guide
- User manual
- Petrol engines 1.3 l
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Carburetors
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Petrol engines 1.6/1.8 l
- Engine repair
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- 4-speed gearbox 084
- 5-speed gearbox 085
- 4-speed gearbox 020/4R
- 5-speed gearbox 020/4T
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Car suspension
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- General information
- Characteristics
- Car care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Engine 1.05/1.30
- Engine 1.60/1.80
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Steering
- Suspension
- Body
- Body and equipment
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Characteristics
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine adjustment
- Engine 1.1/1.3
- Engine 1.5/1.6/1.8
- Engine electrical equipment
- Cooling system
- Fuel system
- Transmission
- Clutch and manual gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- Body
- Body and equipment
- Optional equipment
- General information
- Specifications
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Exhaust and turbocharger
- Cooling system
- Fuel system
- Fuel injection system
- Transmission
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Suspension and wheels
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Heating and ventilation
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting system
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •