Golf 1 (1974-1984, diesel)
Golf 1 (1974-1984, petrol)
Golf 2 (1984-1993, petrol)
Golf 2 (1984-1993)
Golf 3 (1991-1997)
Golf 4 (1997-2004)
Golf 5 (2003-2008)
Car diesel engine repair Volkswagen Golf 3
Suction motor with a displacement of 1.9 liters
The engine compartment of a 47 kW suction motor is shown here: 1 - fuel filter 2 - oil filler neck 3 - suction manifold 4 - pressure regulator valve of the engine crankcase...
The engine compartment of a 47 kW suction motor is shown here: 1 - fuel filter 2 - oil filler neck 3 - suction manifold 4 - pressure regulator valve of the engine crankcase...
Turbodiesel with a displacement of 1.9 liters
The following parts are located in the engine compartment of a 55 kW turbodiesel: 1 - fuel filter 2 - oil filler neck 3 - suction manifold 4 - pressure regulator valve of the...
The following parts are located in the engine compartment of a 55 kW turbodiesel: 1 - fuel filter 2 - oil filler neck 3 - suction manifold 4 - pressure regulator valve of the...
Diesel engine. general information
Two diesel engines are available for the Golf/Vento diesel models. Both engines comply with stringent regulations regarding the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases and...
Two diesel engines are available for the Golf/Vento diesel models. Both engines comply with stringent regulations regarding the content of harmful substances in exhaust gases and...
Diesel principle
Intake stroke: In contrast to a petrol engine, a diesel engine draws in only clean air during this stroke. A gasoline engine, on the other hand, sucks the already prepared...
Intake stroke: In contrast to a petrol engine, a diesel engine draws in only clean air during this stroke. A gasoline engine, on the other hand, sucks the already prepared...
Cylinder block
The diesel cylinder block is made of cast iron. In its lower part is the crankshaft; top working cylinders (four in a row). Around them are channels for coolant, which are also...
The diesel cylinder block is made of cast iron. In its lower part is the crankshaft; top working cylinders (four in a row). Around them are channels for coolant, which are also...
Crankshaft
The task of the crankshaft is to convert the translational motion of the pistons in the cylinders into rotational motion. Connecting rods leading to the cylinders of the...
The task of the crankshaft is to convert the translational motion of the pistons in the cylinders into rotational motion. Connecting rods leading to the cylinders of the...
Pistons
The pistons are made of light metal and have a steel insert that reduces the thermal expansion of the piston. The pistons of diesel engines have as a feature on the upper plane a...
The pistons are made of light metal and have a steel insert that reduces the thermal expansion of the piston. The pistons of diesel engines have as a feature on the upper plane a...
Cylinders
Cylinders, as already mentioned, are part of the cylinder block. The four cylinder bores are the guides for the pistons and are ground in a special way. The walls do not have to...
Cylinders, as already mentioned, are part of the cylinder block. The four cylinder bores are the guides for the pistons and are ground in a special way. The walls do not have to...
Cylinder head gasket
It serves to ensure that the high pressure of the gases in the combustion chamber does not affect the oil and coolant channels in the cylinder head. Sectional view of valve...
It serves to ensure that the high pressure of the gases in the combustion chamber does not affect the oil and coolant channels in the cylinder head. Sectional view of valve...
Cylinder head and camshaft
For reasons of lightness and for better thermal conductivity, the cylinder head is cast from light metal. The valve seats are installed when the cylinder head is heated, so that...
For reasons of lightness and for better thermal conductivity, the cylinder head is cast from light metal. The valve seats are installed when the cylinder head is heated, so that...
Toothed belt
The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. This timing belt with steel wire inserts is of great importance for diesel engine. The engine's small combustion...
The camshaft is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft. This timing belt with steel wire inserts is of great importance for diesel engine. The engine's small combustion...
Hydraulic pushers
Diesel engines are equipped with so-called "cup" pushers, in which a hydraulic valve clearance compensator is built. This device eliminates the need for valve clearance control....
Diesel engines are equipped with so-called "cup" pushers, in which a hydraulic valve clearance compensator is built. This device eliminates the need for valve clearance control....
Lubrication system
In the engine, a number of bearings and rubbing pairs require lubrication. Engine oil is pumped there under pressure from the oil pump. The pump sucks oil through the oil strainer...
In the engine, a number of bearings and rubbing pairs require lubrication. Engine oil is pumped there under pressure from the oil pump. The pump sucks oil through the oil strainer...
Crankcase ventilation
Engine crankcase ventilation avoids overpressure in the crankcase (due to pressure loss during combustion). Gases are supplied to the air filter housing and from there they enter...
Engine crankcase ventilation avoids overpressure in the crankcase (due to pressure loss during combustion). Gases are supplied to the air filter housing and from there they enter...
Checking the engine for oil loss
Unwanted sources of oil are most likely to be found on a diesel engine in the following places: Sealing ring (stuffing box) crankshaft at the flywheel, oil protrudes between the...
Unwanted sources of oil are most likely to be found on a diesel engine in the following places: Sealing ring (stuffing box) crankshaft at the flywheel, oil protrudes between the...
Running in a new engine
Cylinder walls, as well as pistons with piston rings in the initial state, have microscopic roughness on their surfaces. After the initial run, these small irregularities are...
Cylinder walls, as well as pistons with piston rings in the initial state, have microscopic roughness on their surfaces. After the initial run, these small irregularities are...
Engine life
Diesel engines have a mileage of at least 100,000 to 150,000 km. Vehicles that, during operation, have a small number of cold starts and. as a rule, they are operated at a low...
Diesel engines have a mileage of at least 100,000 to 150,000 km. Vehicles that, during operation, have a small number of cold starts and. as a rule, they are operated at a low...
Compression pressure measurement
Compression measurement in the engine cylinders will give an answer to the question of whether the valves and piston rings still seal well. First of all, the ease of starting a...
Compression measurement in the engine cylinders will give an answer to the question of whether the valves and piston rings still seal well. First of all, the ease of starting a...
Engine Troubleshooting
Low pressure Uniformly low compression pressure is certainly not an alarm; the reason may be the difference in the measurements of different instruments. It is doubtful when the...
Low pressure Uniformly low compression pressure is certainly not an alarm; the reason may be the difference in the measurements of different instruments. It is doubtful when the...
Diagnostics of malfunctions of a gear belt
The timing belt is of great importance for a diesel engine, if the belt breaks or slips one or more teeth on the pulley, then severe engine damage inevitably occurs. because the...
The timing belt is of great importance for a diesel engine, if the belt breaks or slips one or more teeth on the pulley, then severe engine damage inevitably occurs. because the...
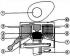
Diagnostics of malfunctions of a laying of a head of the block of cylinders
1 - valve cover 2 - gasket Cylinder head gasket defects occur mainly as a result of overheating, possibly due to the fact that coolant leakage due to the absence of a coolant...
1 - valve cover 2 - gasket Cylinder head gasket defects occur mainly as a result of overheating, possibly due to the fact that coolant leakage due to the absence of a coolant...
Work on the cylinder head
Most work on the cylinder head requires a torque wrench. To completely remove the head, an additional long wrench is required to unscrew the bolts with an internal polyhedron T55....
Most work on the cylinder head requires a torque wrench. To completely remove the head, an additional long wrench is required to unscrew the bolts with an internal polyhedron T55....
Bearing damage
A knocking sound from the engine compartment, which becomes louder with warmer oil, is an indication of bearing damage. Almost always this is a defect in the connecting rod plain...
A knocking sound from the engine compartment, which becomes louder with warmer oil, is an indication of bearing damage. Almost always this is a defect in the connecting rod plain...
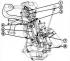
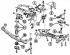
Removal and installation of the engine
1 - right engine console 2 - casing (not installed on our models) 3 - gearbox support 4 - rubber-metal support 5 - left gearbox console 6 - rubber-metal support 7 - aggregate beam...
1 - right engine console 2 - casing (not installed on our models) 3 - gearbox support 4 - rubber-metal support 5 - left gearbox console 6 - rubber-metal support 7 - aggregate beam...
Turbocharged diesel engine
Diesel engines have been using internal mixing in the swirl chamber and combustion chamber for a relatively long time (compared to petrol engine). The maximum number of...
Diesel engines have been using internal mixing in the swirl chamber and combustion chamber for a relatively long time (compared to petrol engine). The maximum number of...
Boost pressure regulator
The chosen design of the turbocharger has the good property that already at a relatively low speed the charge air enters the cylinders, which means that at a high speed there will...
The chosen design of the turbocharger has the good property that already at a relatively low speed the charge air enters the cylinders, which means that at a high speed there will...
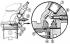
Removing the turbo
1 - turbocharging shaft 2 - turbine wheel on the exhaust side 3 - oil supply channel 4 - turbine wheel on the suction side Cleanliness must be especially observed when working on...
1 - turbocharging shaft 2 - turbine wheel on the exhaust side 3 - oil supply channel 4 - turbine wheel on the suction side Cleanliness must be especially observed when working on...
Troubleshooting
If the turbodiesel engine gives really low power or maximum power is not reached, then the cause may be a defective turbo, what possible faults can be taken into account, we will...
If the turbodiesel engine gives really low power or maximum power is not reached, then the cause may be a defective turbo, what possible faults can be taken into account, we will...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections from other manuals for VW cars:
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Sharan 1 (1995-2000)
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T3 (1979-1992)
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Sharan 1 (1995-2000)
Diesel engines: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T3 (1979-1992)
Golf 5
Golf 4
Golf 3
Golf 2
Golf 2 (petrol)
Golf 1 (petrol)
Golf 1 (diesel)
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling and ventilation system
- Fuel system
- Ignition system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Body
- Interior (internal elements)
- Exterior (external elements)
- Doors and covers
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Washers and wipers
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Weekly checks
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines
- Diesel engines
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (petrol)
- Control system (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Ventilation and heating
- Car doors and sunroof
- Washers and glass cleaners
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- Petrol engine
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engine
- Engine repair
- Diesel injection system
- Pre-glow system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Gearbox and drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Wheels and suspension
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to guide
- User manual
- Petrol engines 1.3 l
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Carburetors
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Petrol engines 1.6/1.8 l
- Engine repair
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- 4-speed gearbox 084
- 5-speed gearbox 085
- 4-speed gearbox 020/4R
- 5-speed gearbox 020/4T
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Steering
- Car suspension
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices
- General information
- Characteristics
- Car care
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Engine 1.05/1.30
- Engine 1.60/1.80
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Brake system
- Steering
- Suspension
- Body
- Body and equipment
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Characteristics
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine adjustment
- Engine 1.1/1.3
- Engine 1.5/1.6/1.8
- Engine electrical equipment
- Cooling system
- Fuel system
- Transmission
- Clutch and manual gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Chassis
- Steering
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- Body
- Body and equipment
- Optional equipment
- General information
- Specifications
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Exhaust and turbocharger
- Cooling system
- Fuel system
- Fuel injection system
- Transmission
- Clutch and drive shafts
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Suspension and wheels
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Heating and ventilation
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting system
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •