A number of special tools are needed, without which it is extremely difficult to carry out the work.
Drain gear oil before disassembly. To do this, use an Allen wrench (17 mm), to remove the drain plug. Remove all dirt from the outside of the gearbox.
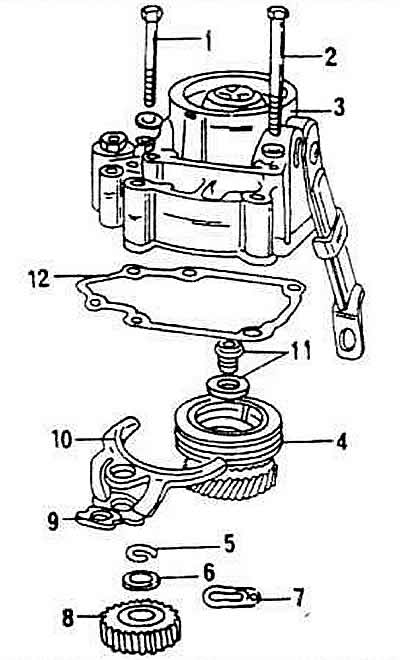
Gearcase cover and fifth gear
1 - screw M8 x 62, 25 Nm
2 - screw M8 x 65, 25 Nm
3 - gearbox housing cover
4 - fifth gear synchronizer with thrust gear
5 - retaining ring (only for 1.8L engine)
6 - thrust washer (only for 1.8L engines)
7 - locking plate (only for 2L 85kW engine)
8 - fifth gear
9 - lock washer, must be replaced
10 - fifth gear engagement fork
11 - M7 screw with washer, 150 Nm
12 - seal, must be replaced
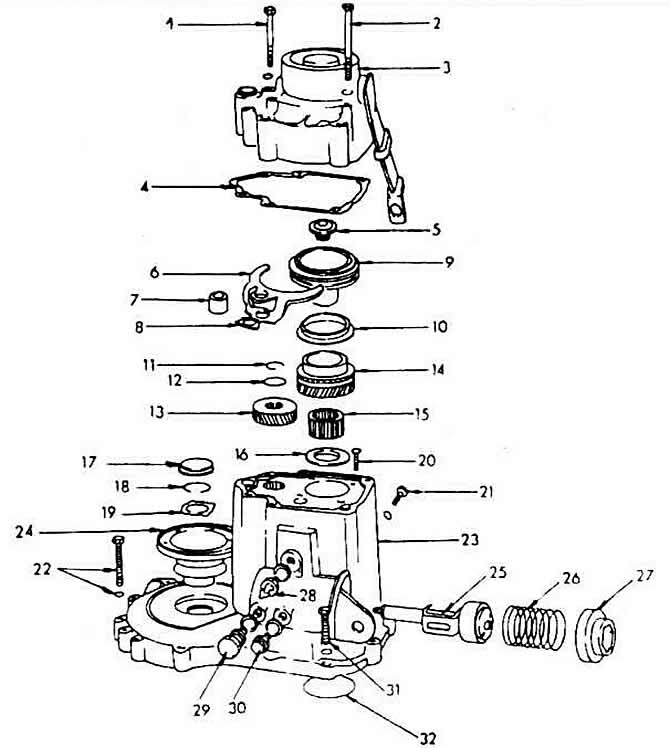
Transmission housing and shift shaft
1 - screw, 25 Nm
2 - screw, 25 Nm
3 - gearbox housing cover
4 - seal
5 - screw, 150 Nm
6 - fifth gear engagement fork
7 - spacer sleeve
8 - locking plate
9 - fifth gear switch
10 - 5th gear synchronizing ring
11 - snap ring
12 - thrust washer
13, 14 - fifth gear gears
15 - needle roller bearing
16 - thrust washer
17 - cover, subject to mandatory replacement
18 - snap ring
19 - shaped washer
20 - screw, 15 Nm
21 - screw, 30 Nm
22 - screw, 25 Nm
23 - gearbox housing
24 - drive side flange
25 - switch shaft
26 - spring
27 - case
28 - reverse switch
29 - fifth gear locking screw
30 - locking screw of the shift shaft
31 - screw, 25 Nm
32 - compensation washer
Disassembly of the gearbox housing
Disconnect the gearbox housing cover screws and remove the cover together with the seal.
Unscrew the blocking plug for the shift shaft from the side of the gearbox housing.
Unscrew the reverse light switch.
Using a socket wrench, unscrew the shift shaft cap. Remove the spring, move the fork to the idle position and pull out the shift shaft. The forks must be moved to the idle position, otherwise it will not be possible to pull out the shaft. Unscrew the tachometer drive directly above the blocking plug of the shift shaft.
Remove the screw «Torx», used to mount the reversing vase.
Remove the flange on the drive side located in the area of the clutch release mechanism. To do this, press the middle plug out of the flange and remove the circlip that holds the flange against the drive shaft.
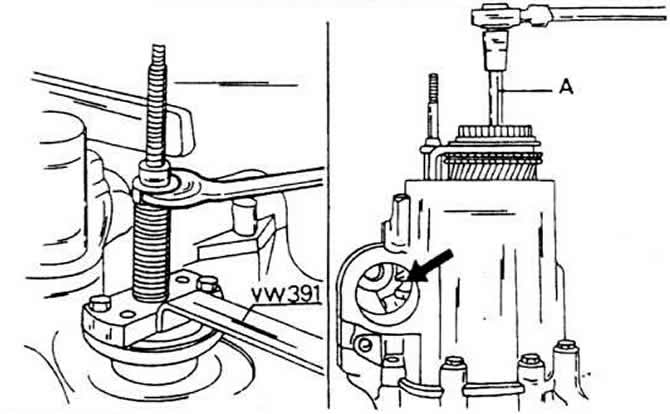
Disconnect multi-toothed (polygonal) key (12 mm) screw on the inside of the switch sleeve. Since the screw is well tightened, such a push-on tip must be trimmed so that it can be inserted into the head (on right).
To stop the shaft, insert the fifth gear (push the sliding sleeve down) and also insert the reverse gear (push the power plug through the hole from the left down).
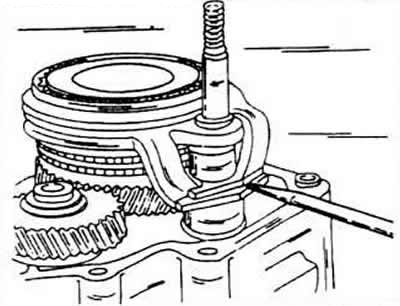
Press the locking plate to fix the switching tube downwards with a screwdriver.
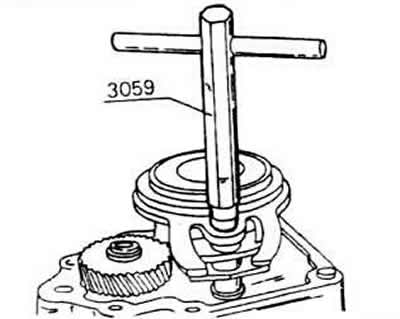
Unscrew the switching tube using special key 3059. Turn the key to the left. The switch bar does not need to be removed from the tube.
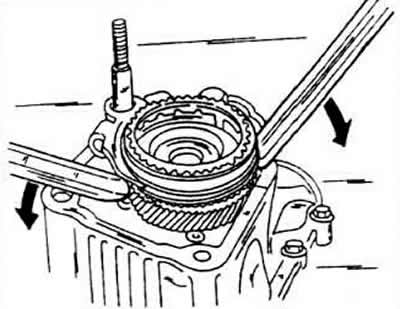
Pull out the shifter sleeve together with the fifth gear and the shift fork. To do this, place a lever under the assembly to wring it out. before you can lift it straight up. When doing this, be careful not to damage the gearbox housing. There is a thrust washer under the switch bushing.
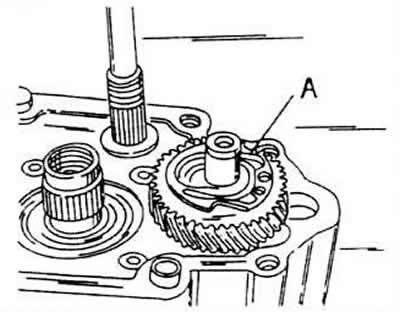
Remove the circlip and 5th gear thrust washer. In case of dismantling the crankcase of a 2 liter engine, hold the gear with a locking device.
Remove the fifth gear from the shaft using a two-arm removable tool.
Using a key with an internal hexagon (6 mm) unscrew the clamping plate of the input shaft bearing. Four screws must be removed.
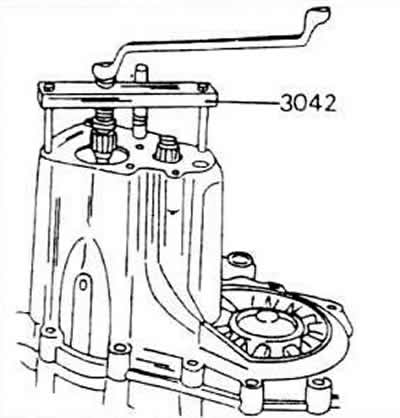
Disconnect the mounting screws of the gearbox housing and remove the housing. If the crankcase cannot be removed by tapping it with a plastic hammer, you need to use a removable tool that is installed. The gearbox housing is now disassembled into two halves and further repair or adjustment operations can be carried out as described in the relevant sections.
If the gearbox housing, bearing housing and drive shaft are replaced, the thickness of the wear washer on the bearing ring must be re-determined.
Dismantling the input shaft
With the gearbox housing dismantled, the input shaft is removed as follows.
Remove the switch bar. It is held by two springs in the floating position (one in the gearbox housing, and the second in the bearing shield).
Remove the switching bar from the bearing shield and take out the complete set of switching forks from the side.
Disconnect the 4th gear snap ring from the top side of the engine.
Remove the front shaft along with the fourth gear (this is the pinion gear). When doing this, note that the reverse gear does not mesh with the teeth of other shafts. Move the reverse gear if necessary.
Dismantling the output shaft
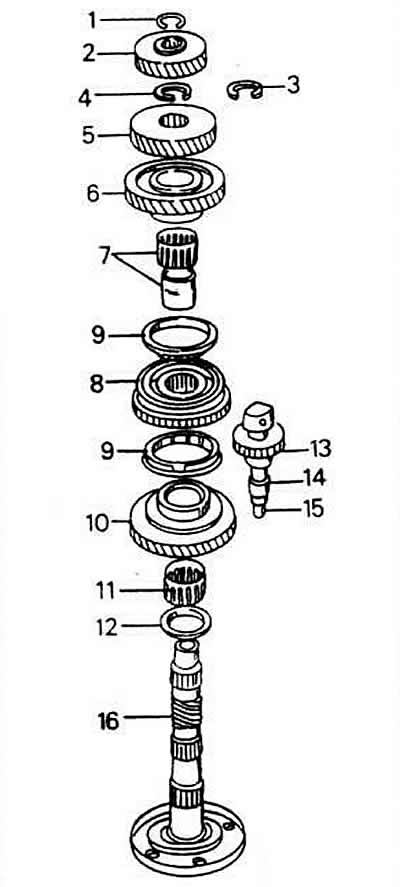
Output shaft mounting scheme
1 - snap ring
2 - fourth gear
3 - additional snap ring
4 - snap ring
5 - third gear
6 - second gear gear
7 - needle roller bearing
8 - synchronizer, first-second gear
9 - synchronizing rings
10 - gear, first gear
11 - needle roller bearing
12 - thrust washer
13 - reverse gear
14 - thrust sleeve
15 - reverse shaft
16 - secondary shaft
It is necessary to dismantle the entire set of gears before the output shaft can be removed from the bearing shield.
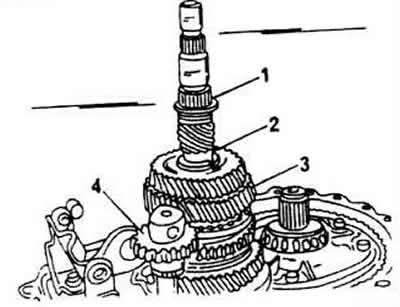
Dismantle the snap ring of the fourth gear of the secondary shaft and remove the gear. Follow it up right away. that the gear must be placed with the shoulder up. In a 2 liter engine gearbox, the diameter of the input shaft is larger, therefore the inner diameter of the gears is larger. In addition, a second snap ring 3 is used for fastening. In this case, the parts must be dismantled as follows:
Remove circlip 1 before removing third gear.
Remove circlip 2 from third gear.
Remove the synchronizing ring and needle roller bearing 3 from the third and second gear shaft.
Remove the reverse gear 4 together with the shaft. If necessary, use a rubber mallet, with the reverse gear in the position shown in the figure, i.e. it must be against the stop.
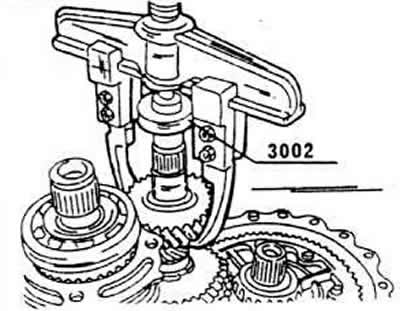
In other transmissions, if necessary, the gear can be removed using a two-tooth puller.
There is a second snap ring under the gear, which should also be removed. Its thickness may vary. The ring serves to adjust the axial clearance of the third gear, which must be respected. In this gearbox, the ring has a larger diameter.
Remove the third gear. Follow up right away. so that the bead of the gear is pointing down, i.e. to the second gear.
Remove the 2nd gear with needle roller bearing.
Remove the reverse shaft together with the reverse gear. At the same time, knock the shaft out of the bearing housing with a plastic hammer.
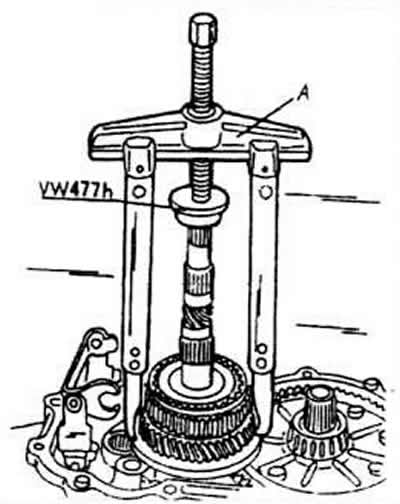
With a two prong puller and a suitable pressure boss placed on the end of the shaft (arrow), remove the first gear and the first-second synchronizer at the same time.
Remove the first gear needle bearing and thrust washer. Pay attention to the position of the thrust washer.
Unscrew the gearbox bearing cover. Use four screws for fastening. Remove the cover.
Remove the shaft from the bearing housing.
Removing the differential
Remove the differential input shaft flange in the same way. as described in the case of dismantling the gearbox housing. Raise the differential together with the final drive gear. The primary and secondary shafts must first be dismantled.
The bevel pinion shaft is held in place by two elongated flat bevel gear rivets.
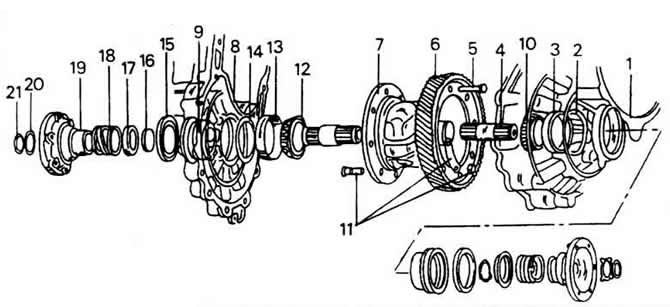
1 - bearing shield
2 - compensation washer S2
3 - working ring of the bearing
4 - drive shaft for flange
5 - rivet (only during production)
6 - flat bevel gear
7 - differential box
8 - gearbox housing
9 - tin sleeve
10 - tapered roller bearing
11 - screw and nut, 70 Nm
12 - tapered roller bearing
13 - bearing working ring
14 - compensation washer S1
15 - oil sealing ring
16 - conical ring
17 - thrust ring
18 - compression spring
19 - drive side flange
20 - shaped washer
21 - snap ring
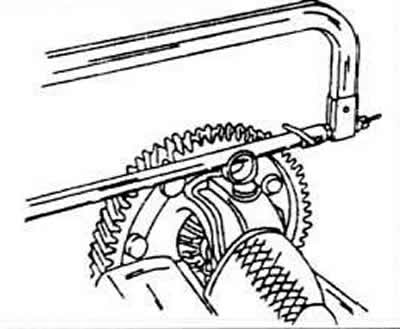
Saw off both rivets to the same length with respect to the differential axle and knock the axle out of the crankcase. Make sure that no sawdust gets into the differential bearing.
Remove the circlips from the inside of the differential.
Remove the differential gears and remove the plastic carrier.
The differential bearings can be removed using a two-arm puller.
Disassembly of the input shaft
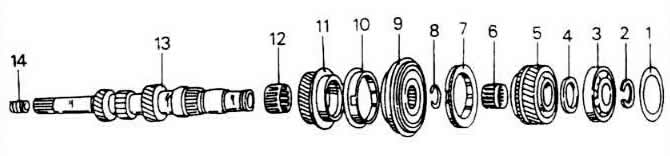
1 - compensation washer
2 - snap ring
3 - ball bearing
4 - thrust washer
5 - fourth gear
6 - needle roller bearing
7 - 4th gear timing ring
8 - snap ring
9 - synchronizer of the third-fourth gear
10 - synchronizing ring of the third gear
11 - third gear
12 - needle roller bearing
13 - input shaft
14 - sleeve
The input shaft of the gearbox has a thickening in the areas of the finely splined profile of the drive disc, oil sealing ring and front needle roller bearing.
Press out ball bearing 3 under pressure. To do this, insert the upsetting plates of the press between the bearing and the fourth gear.
Using a press, press out the fourth gear 5, but this time place the upsetting plates under the gear.
Remove needle roller bearing 6.
Remove the circlip 8 used to secure the 3rd/4th gear synchronizer. Press out the synchronizer 9. The upsetting plates are inserted under the third gear.
Remove needle roller bearing 12.

Visitor comments