Air conditioning system diagram
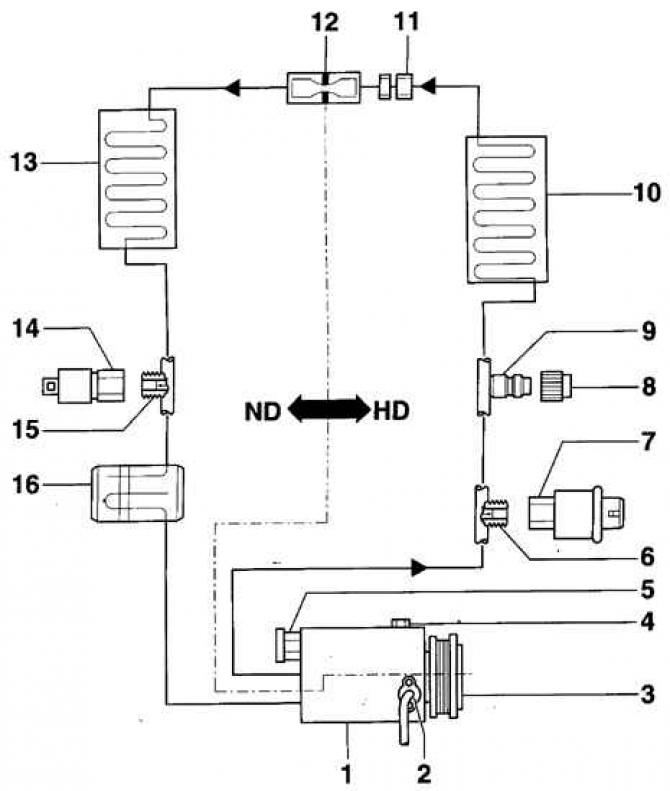
- 1 - compressor;
- 2 - air conditioner compressor rotation speed sensor;
- 3 - electromagnetic clutch;
- 4 - oil drain plug;
- 5 - overpressure valve;
- 6 - connection with the valve;
- 7 - push-button switch for air conditioner and electromagnetic clutch;
- 8 - cap;
- 9 - service connection;
- 10 - capacitor;
- 11 - pipeline connection;
- 12 - throttle;
- 13 - evaporator;
- 14 - push button switch for the cooling circuit;
- 15 - valve connection;
- 16 - capacity;
- HD - high pressure side;
- ND - low pressure side
The air conditioning system removes excess heat and moisture from the passenger compartment in accordance with basic physical principles. The refrigerant circulating as a liquid in the high pressure portion of the system evaporates and turns into a gas in the low pressure portion. When the gas expands, cooling occurs, accompanied by the removal of heat from the air supplied by the fan to the passenger compartment and a decrease in its temperature. Further, as it passes through the condenser, the refrigerant gives off the absorbed heat to the surrounding air. The heat extraction cycle continues indefinitely as the refrigerant circulates in a closed circuit. From the air supplied to the passenger compartment, moisture is removed due to condensation on the evaporator of the refrigerator compartment.
The air conditioning system is a potential hazard. Its maintenance requires compliance with certain rules. Most air conditioning repairs and maintenance require specialized equipment and skills.
Body ventilation is provided by the formation of a through air flow. Fresh air enters the car through an air intake located in front of the windshield. The air flow exits through the exhaust channels located on the sides of the body near the rear shock absorbers.
The amount of air flow is controlled by a four-speed fan.
The mixed type air heating system is designed to quickly respond to changes in the air temperature in the passenger compartment and reduce the temperature pulsation of the heated air. The coolant of the engine cooling system constantly circulates in the heater core and the coolant flow is not regulated. The controlled factor is the air temperature, which is changed by the mixing damper, which determines the amount of air passing through the heater radiator before it enters the car interior.
To prevent fresh air from entering the car interior, there is an air recirculation mode.
Air Conditioning System Maintenance Precautions
The air conditioning system is charged with refrigerant "Freon R12", and the parts of the system are under a working pressure of over 300 atmospheres. The high pressure and chemical attack of the refrigerant is a source of increased danger when the system is not properly serviced by untrained technical personnel and when using improper equipment.
Automotive coolant "Freon R12" has a hazardous effect on the environment. In order to protect the environment, Volkswagen prescribes the use of equipment for disposal and recycling, equipped with an insurance laboratory certificate, when the air conditioning system is depressurized (UL).
Warning: The air conditioning system must only be serviced by trained technicians who are trained in safe work practices, using the proper equipment, following depressurization procedures, and who are familiar with the collection and storage of automotive refrigerant.
Warning: Avoid skin contact with refrigerant.
Warning: Wear protective goggles when working near the air conditioning system.
Warning: If refrigerant comes into contact with skin or eyes, do not rub the affected area. Rinse immediately with cold water for at least 15 minutes. Contact a doctor or health facility immediately. Self-medication is not allowed.
Warning: The refrigerant is stored under pressure in a new cylinder. Store the cylinder at a temperature not exceeding 50°C. Take care not to drop the cylinder from a height or otherwise cause damage to the cylinder.
Warning: Work should be carried out in a well-ventilated area. The refrigerant evaporates quickly, resulting in reduced oxygen supply and difficulty breathing.
Warning: The gaseous refrigerant is heavier than air and must collect relatively quickly at the bottom, such as under a car.
Warning: Combustion of refrigerant produces poisonous gas. Keep refrigerant away from open flames. Do not smoke. When using a flame leak detector, avoid breathing smoke.
Warning: When welding near an air conditioning system, always remove refrigerant from it. Electric welding near refrigerant piping may cause the refrigerant to decompose due to ultraviolet radiation.
Warning: Do not expose parts of the air conditioning system to high temperatures or open flames. Overheating can cause system pressure to rise and ignite.
Warning: Cleaning the condenser or evaporator with steam is not allowed. Use only cold water or compressed air.

Visitor comments