Catalyst
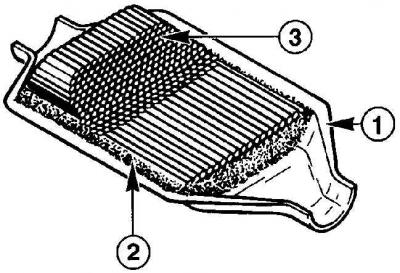
- 1 - body;
- 2 - seal;
- 3 - honeycomb catalyst
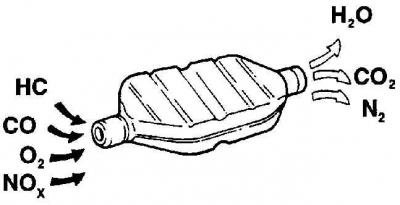
Elements included in the catalyst and products leaving the catalyst
Catalysts are installed on all cars to reduce the amount of harmful substances emitted into the atmosphere with exhaust gases.
The exhaust gas catalyst has a stainless steel casing to which are welded inlet and outlet cones with nozzles and mounting flanges, as well as heat reflectors holding the ceramic lining. The entire internal volume of the case is occupied by a ceramic porous monolith, fixed with stainless steel rings or mesh. The structure of the monolith is a conventional filter, but the entire inner and outer surface of the pores in contact with gases is covered with a very thin molecular layer of an alloy that contains platinum, rhodium and palladium. The porous monolith has a large surface area covered with this alloy of very expensive metals, which mainly determines the high price of catalysts.
A reaction takes place in the catalyst that converts potentially hazardous hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide in the exhaust gases into harmless gases and water vapour.
The engine emits into the atmosphere together with exhaust gases products of complete (water vapor H2O, nitrogen N2, etc.) and incomplete (carbon monoxide CO, as well as CnHm, nitrogen oxides NOX) fuel combustion. The total number of components contained in these gases exceeds several hundred, and most of them are harmful to human health.
Exhaust gases, penetrating through the porous surface of the monolith, firstly, heat it, and secondly, are additionally oxidized. From CO, CO2 is obtained, that is, non-toxic carbon dioxide, CnHm passes into CO2 and H2O in several stages, NOX turns into molecular N2, which is contained in ordinary air, and into water. In a word, quite complex chemical reactions take place in the catalyst, due to the high temperature and the presence of a special coating of expensive metals.
The main positive effect of the catalyst is the complete neutralization of three components - CO, CnHm, NOX - which are more in the exhaust gases than other harmful substances. And it is achieved not only due to the presence of platinum, rhodium and palladium. An important role is played by the temperature maintained in the range of 300–800°C. If it decreases to 250°C, the chemical reactions of CO, CnHm, NOX neutralization, despite the presence of catalyst metals, will not occur. And at a temperature of about 900°C, the catalytic film begins to melt and break down.
Gasoline engines
On all models with a catalyst, the fuel supply system is of a closed type, that is, based on a signal from an oxygen sensor installed in the exhaust system, the control unit constantly optimizes the composition of the fuel-air mixture. Depending on the oxygen content in the exhaust gases, the oxygen sensor induces a voltage of 0.1 V (high oxygen, lean mixture) up to 0.9 V (low oxygen, rich mixture). Based on this data, the engine control unit changes the opening time of the fuel injectors and changes the fuel ratio in the fuel-air mixture. The metric ratio of the fuel mixture, at which its complete combustion occurs and there are no harmful substances in the exhaust gases, is 14.7 parts by weight of air per 1 part of fuel.
The catalyst works effectively at temperatures from +300°С to +800°С.
Diesel engines
On vehicles with diesel engines, exhaust gas treatment is carried out by an unregulated oxidizing catalyst.
Reducing the percentage of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases of a diesel engine is achieved by installing a re-burning system for part of the exhaust gases on the vehicle (EGR). The EGR valve of the exhaust gas reburning system is installed in the elbow of the exhaust system and is controlled by a vacuum regulator. The EGR valve on a warm engine directs part of the exhaust gases into the engine's combustion chambers, resulting in a decrease in temperature and, at the same time, the percentage of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases.
Operation of vehicles with a catalyst
The catalyst is a reliable and simple device that does not need any maintenance, but there are some facts that the owner must be aware of in order to maximize the life of the catalyst.
Do not use leaded gasoline in a vehicle equipped with a catalyst, as the lead will coat the precious metals in the catalyst lattice, reducing their conversion efficiency and eventually damaging the catalyst.
Always keep the ignition and fuel system in perfect order.
If misfiring is observed while the engine is running, do not operate the vehicle until the problem is corrected.
If the engine control warning lamp lights up while the engine is running, contact a service station as soon as possible. If there is damage to the engine management, then in addition to increasing fuel consumption and reducing the dynamic characteristics of the engine, the catalyst may fail.
Do not start the engine by towing.
Do not turn off the ignition at high engine speeds.
Do not use fuel and engine oil additives, as additives may contain substances that can damage the catalyst.
Do not drive the vehicle if a trail of blue smoke is visible from the exhaust pipe.
After stopping the engine, the exhaust system continues to emit a significant amount of heat for a long time, so you should avoid parking the car on grass and dry leaves. Remember that the catalytic converter is fragile, so avoid hitting when removing the catalytic converter or exhaust system.
The catalyst used on a well-adjusted car should last from 100 to 160 thousand kilometers of the car.

Visitor comments