Passat B2 (1981-1988)
Passat B3 (1988-1993)
Passat B4 (1988-1996)
Passat B5 (1996-2005)
Passat B6 (2005-2010)
Engine 4-cylinder car Volkswagen Passat B2
Design and technical characteristics. General information
A four-stroke, four-cylinder, carburetor, in-line engine is installed with an inclination to the right along the longitudinal axis of the car. The cooling system is liquid. The...
A four-stroke, four-cylinder, carburetor, in-line engine is installed with an inclination to the right along the longitudinal axis of the car. The cooling system is liquid. The...
Specifications of the cylinder head
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy. Seats and valve guides are pressed into the cylinder head. The cylinder head gasket is installed with the inscription «oben» («top»)...
The cylinder head is cast from aluminum alloy. Seats and valve guides are pressed into the cylinder head. The cylinder head gasket is installed with the inscription «oben» («top»)...
Specifications of the cylinder block
The cylinder block is sleeveless, cast iron. In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five supports for the crankshaft main bearing shells. The main bearing caps are...
The cylinder block is sleeveless, cast iron. In the lower part of the cylinder block there are five supports for the crankshaft main bearing shells. The main bearing caps are...
Technical characteristics of the crank mechanism
Crankshaft Crankshaft steel, forged. The shaft is five-bearing. The upper main bearing shells have oil grooves. On the cheeks of the shaft there are four counterweights forged...
Crankshaft Crankshaft steel, forged. The shaft is five-bearing. The upper main bearing shells have oil grooves. On the cheeks of the shaft there are four counterweights forged...
Technical characteristics of the gas distribution mechanism
The engine uses a valve timing mechanism with an overhead camshaft, which is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft pulley. Belt tension is provided by an eccentric roller....
The engine uses a valve timing mechanism with an overhead camshaft, which is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft pulley. Belt tension is provided by an eccentric roller....
Specifications of the lubrication system
The engines have a pressure lubrication system. Under vacuum, the oil is sucked in through the strainer of the oil receiver from the oil sump and pumped by the gear oil pump into...
The engines have a pressure lubrication system. Under vacuum, the oil is sucked in through the strainer of the oil receiver from the oil sump and pumped by the gear oil pump into...
Specifications of the cooling system
The engine uses a liquid cooling system with forced circulation. The cooling system includes an engine water jacket, a radiator, an expansion tank, a centrifugal water pump, a...
The engine uses a liquid cooling system with forced circulation. The cooling system includes an engine water jacket, a radiator, an expansion tank, a centrifugal water pump, a...
Power System Specifications
Fuel tank The plastic fuel tank is mounted behind the rear axle. Fuel tank capacity, l: 60. Fuel pump The diaphragm-type mechanical fuel pump is driven by the countershaft...
Fuel tank The plastic fuel tank is mounted behind the rear axle. Fuel tank capacity, l: 60. Fuel pump The diaphragm-type mechanical fuel pump is driven by the countershaft...
Technical characteristics of carburetors
Carburetor Keihin 26-30 DC The EP model engine was equipped with a Keihin 26-30 DC emulsion-type carburetor, two-chamber, with sequential opening of throttle valves. The...
Carburetor Keihin 26-30 DC The EP model engine was equipped with a Keihin 26-30 DC emulsion-type carburetor, two-chamber, with sequential opening of throttle valves. The...
Specifications of the ignition system
The ignition system is non-contact, including a distribution sensor with a built-in electronic control pulse sensor, an ignition coil and a switch. Characteristics of automatic...
The ignition system is non-contact, including a distribution sensor with a built-in electronic control pulse sensor, an ignition coil and a switch. Characteristics of automatic...
Tightening torques of the main threaded connections, kgf.m
Cylinder head bolts: 1st reception: 4.0; 2nd reception: 6.0; Step 3: turn 180°. Bolt of fastening of a gear pulley of a cranked shaft: 20,0. Nuts of hairpins of fastening of cases...
Cylinder head bolts: 1st reception: 4.0; 2nd reception: 6.0; Step 3: turn 180°. Bolt of fastening of a gear pulley of a cranked shaft: 20,0. Nuts of hairpins of fastening of cases...
Checking and adjusting clearances in the valve drive mechanism
Examination Warm up the engine to operating temperature (the coolant temperature is above +35°C, the cylinder head must be warm to the touch). Disconnect the fuel supply hose from...
Examination Warm up the engine to operating temperature (the coolant temperature is above +35°C, the cylinder head must be warm to the touch). Disconnect the fuel supply hose from...
Fuel pump supply system
The fuel pump is fastened with two nuts through a heat-insulating gasket and an o-ring. Pump housing and cover are one-piece, i.e. the pump cannot be repaired and, in case of a...
The fuel pump is fastened with two nuts through a heat-insulating gasket and an o-ring. Pump housing and cover are one-piece, i.e. the pump cannot be repaired and, in case of a...
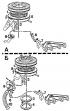
The principle of operation of the Keihin 26-30 DC carburetor
Design features and calibration data of the Keihin 26-30 DC carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Starting device The enrichment of the combustible...
Design features and calibration data of the Keihin 26-30 DC carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Starting device The enrichment of the combustible...
Keihin 26-30 DC carburetor adjustment
Air damper starting gap adjustment Fully pull out the choke control handle; at the same time, the air damper control lever should be at the stop. Press the starter rod all the way...
Air damper starting gap adjustment Fully pull out the choke control handle; at the same time, the air damper control lever should be at the stop. Press the starter rod all the way...
The principle of operation of the Pierburg 1VZ carburetor
Design features and calibration data of the carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Starting device When starting a cold engine under the influence...
Design features and calibration data of the carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Starting device When starting a cold engine under the influence...
Checking and adjusting the Pierburg 1VZ carburetor
Checking the fuel level in the float chamber The position of the float in the float chamber is not adjustable. If a malfunction is detected, check the tightness of the float and...
Checking the fuel level in the float chamber The position of the float in the float chamber is not adjustable. If a malfunction is detected, check the tightness of the float and...
The principle of operation of the Pierburg 2B5 carburetor
Features of the device and calibration data of the carburetor are indicated in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Drawing « Details of the carburetor 2V5 » given in the...
Features of the device and calibration data of the carburetor are indicated in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Drawing « Details of the carburetor 2V5 » given in the...
Checking and adjusting the Pierburg 2B5 carburetor
Adjusting the fuel level in the float chamber Remove the carburetor cover and turn it over. Measure the distance between the plane of the carburetor cover and the lower point of...
Adjusting the fuel level in the float chamber Remove the carburetor cover and turn it over. Measure the distance between the plane of the carburetor cover and the lower point of...
The principle of operation of the Pierburg 2E2 carburetor
Features of the device and calibration data of the carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Pierburg 2E2 carburetor cover details: 1 - carburetor...
Features of the device and calibration data of the carburetor are given in the subsection « Design and specifications ». Pierburg 2E2 carburetor cover details: 1 - carburetor...
Checking and adjusting the Pierburg 2E2 carburetor
Checking the fuel level in the float chamber The position of the float in the float chamber is not adjustable. If a malfunction is detected, check the tightness of the float and...
Checking the fuel level in the float chamber The position of the float in the float chamber is not adjustable. If a malfunction is detected, check the tightness of the float and...
The device and principle of operation of the electronic ignition system
Device The electronic ignition system includes an ignition distributor with a built-in proximity sensor (pulse generator), switch and high energy ignition coil. Like the...
Device The electronic ignition system includes an ignition distributor with a built-in proximity sensor (pulse generator), switch and high energy ignition coil. Like the...
Removal and installation of the sensor-distributor ignition
Removing Disconnect the spark plug wires and ignition coil wire from the ignition distributor. Unfasten the spring clips and remove the cover of the sensor-distributor. Disconnect...
Removing Disconnect the spark plug wires and ignition coil wire from the ignition distributor. Unfasten the spring clips and remove the cover of the sensor-distributor. Disconnect...
Setting the ignition timing
To set the ignition timing, a stroboscope and a control tachometer are used. Connect the stroboscope and tachometer in accordance with the operating instructions. Start the...
To set the ignition timing, a stroboscope and a control tachometer are used. Connect the stroboscope and tachometer in accordance with the operating instructions. Start the...
Removing and installing the camshaft drive belt
Removing Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and remove the alternator drive belt. Remove the crankshaft pulley. Remove toothed belt guards. Disconnect the high voltage wire...
Removing Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and remove the alternator drive belt. Remove the crankshaft pulley. Remove toothed belt guards. Disconnect the high voltage wire...
Removing the cylinder head
Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Place a container under the engine to collect the coolant and drain the coolant from the cooling system by disconnecting...
Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Place a container under the engine to collect the coolant and drain the coolant from the cooling system by disconnecting...
Installing the cylinder head
Note. Replace the gaskets every time the cylinder head is removed. Install a new cylinder head gasket «oben» («top») towards the plane of the head. Insert bolts 8 and 10 into the...
Note. Replace the gaskets every time the cylinder head is removed. Install a new cylinder head gasket «oben» («top») towards the plane of the head. Insert bolts 8 and 10 into the...
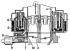
Disassembly and repair of the cylinder head
When disassembling the cylinder head, put marks on the removed parts in order to put them in their original places during assembly. Remove the bearing caps No. 5, 1 and 3 of the...
When disassembling the cylinder head, put marks on the removed parts in order to put them in their original places during assembly. Remove the bearing caps No. 5, 1 and 3 of the...
Cylinder head assembly
Install the valve spring support washers and insert the valves into the valve guides. Using drift 10 204, press new valve stem seals onto the valve guides, then put protective...
Install the valve spring support washers and insert the valves into the valve guides. Using drift 10 204, press new valve stem seals onto the valve guides, then put protective...
Removal and installation of the engine
Removing Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Open the cap of the expansion tank. Disconnect hoses from radiator and drain coolant. Disconnect the electrical...
Removing Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Open the cap of the expansion tank. Disconnect hoses from radiator and drain coolant. Disconnect the electrical...
Engine disassembly
Note. When disassembling, put marks on the parts that are suitable for further use, so that during assembly, install them in their original places and in their original position....
Note. When disassembling, put marks on the parts that are suitable for further use, so that during assembly, install them in their original places and in their original position....
Engine Assembly
Checking cylinder diameters Accurately measure cylinder diameters. Measurements to be made with a caliper in three belts as in the transverse direction «A», and in the...
Checking cylinder diameters Accurately measure cylinder diameters. Measurements to be made with a caliper in three belts as in the transverse direction «A», and in the...
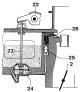
Removal and installation of the oil pump
Removing the oil pump The oil pump can be removed directly on the vehicle. Drain the oil from the engine crankcase. Remove the lower clutch housing cover. Install the jack under...
Removing the oil pump The oil pump can be removed directly on the vehicle. Drain the oil from the engine crankcase. Remove the lower clutch housing cover. Install the jack under...
Dismantling, checking the technical condition and assembling the oil pump
Remove the two bolts securing the oil pump cover to the housing. Separate the cover from the body. Remove drive shaft and oil pump drive gear. Wash the pump housing with gasoline....
Remove the two bolts securing the oil pump cover to the housing. Separate the cover from the body. Remove drive shaft and oil pump drive gear. Wash the pump housing with gasoline....
Coolant replacement
Remove the expansion tank cap. Disconnect the radiator inlet hose from the thermostat housing and drain the fluid. Check the tightness of the cooling system hose clamps. Fill the...
Remove the expansion tank cap. Disconnect the radiator inlet hose from the thermostat housing and drain the fluid. Check the tightness of the cooling system hose clamps. Fill the...
Removal and installation of the water pump
Drain the liquid from the cooling system. Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Remove generator. Disconnect hoses from water pump. Loosen the pump mounting...
Drain the liquid from the cooling system. Disconnect the wire from the negative battery terminal. Remove generator. Disconnect hoses from water pump. Loosen the pump mounting...
Disassembly and assembly of the water pump
Remove the pump drive pulley. Loosen the bolts of the pump cover and remove it complete with the bushing, shaft and impeller, disconnect the cover from the gasket plane with light...
Remove the pump drive pulley. Loosen the bolts of the pump cover and remove it complete with the bushing, shaft and impeller, disconnect the cover from the gasket plane with light...
Alternator Drive Belt Tension Adjustment
Loosen the mounting bolts of the bracket and tension bar of the generator. Move the generator away from the cylinder block and tighten the bolt securing the generator to the...
Loosen the mounting bolts of the bracket and tension bar of the generator. Move the generator away from the cylinder block and tighten the bolt securing the generator to the...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections from other manuals for VW cars:
Power unit: Engine 1.5/1.6/1.8 Volkswagen Golf 1 (1974-1984, petrol)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Polo 4 (2001-2009)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Engine 2.0 (petrol) Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Petrol engines 1.6 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Power unit: Engine 1.5/1.6/1.8 Volkswagen Golf 1 (1974-1984, petrol)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Polo 4 (2001-2009)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Engine 2.0 (petrol) Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Petrol engines 1.6 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Passat B6
Passat B5
Passat B4
Passat B3
Passat B2
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Petrol engine 1.6L
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel injection system
- Petrol engine 2.0L
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Fuel and exhaust systems
- Diesel engine 2.0L
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel and exhaust systems
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Wheels and tires
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Weekly checks
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Engine management
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Wheels and tires
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors and covers
- Ventilation and heating
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Technical data
- 8-valve engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Fuel injection «Mono-Jetronic»
- Control system «Mono-Motronic»
- Control system «Digifant»
- Control system «Simos»
- 16-valve engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel injection «K-Jetronic»
- Control system «KE-Motronic»
- Control system «Digifant»
- Diesel engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Power and control system
- Turbocharging system
- Digital control system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox
- Hydromechanical gearbox
- Front wheel drive
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Driving Tips
- Maintenance instructions
- Technical data
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Ignition system
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Petrol injection system
- Diesel engine
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Heating system
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting system
- Equipment and devices
- Wiper system
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to instructions
- User manual
- Power unit
- Engines 4-cylinder FZ
- Engines 4-cylinder
- Engines 5-cylinder
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Four-speed gearbox
- Five-speed gearbox
- Hydromechanical gearbox
- Front wheel drive
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •