Voltage measurement
You can verify the presence of voltage using a simple test lamp or voltage indicator. Thus, first of all, it is found out whether there is a voltage at all. In order to measure the value of the available voltage, it is necessary to connect a voltmeter (voltage measuring instrument). A voltmeter is always included in the universal measuring instrument.
First of all, at the voltmeter it is necessary to set the measurement range in which the measured voltage is supposed to be. The voltage in the car does not exceed, as a rule, about 14 volts. The exception is the ignition system: here the ignition voltage can be up to 30,000 volts. This high voltage can only be measured with a special meter or oscilloscope.
If when using measuring instruments designed specifically for cars, you only need to turn on the voltmeter on the control panel, then when using a universal instrument, a number of decisions must first be made. First of all, a constant voltage area is set on the control panel (DCV instead of ACV corresponding to AC voltage). Then the measurement range is selected. Since in the car, except in the ignition system, there is no voltage of more than 14 volts, the upper value of the set measuring range should be slightly larger (about 15 to 20 volts). If it is reliably known that the measured voltage is significantly lower, for example, about 2 volts, the upper value of the settable measuring range can be reduced in order to obtain a higher measurement accuracy. If the values of the measured voltages exceed the measurement range of the device, the device may fail.
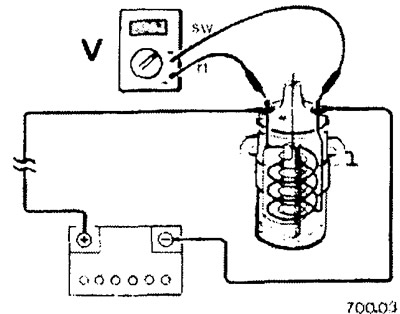
Connect the measuring device cables as shown in the figure in parallel with the power consumer. In this case, the red cable of the device is connected to the conductor going to the positive (+) battery terminal, and the black cable to the ground wire or to the vehicle ground, for example, the engine block. Measurement example: When the engine does not start correctly because the starter turns too slowly, it is advisable to check the battery voltage while the starter is running. To do this, connect the red cable (+) voltmeter to the positive pole of the battery and black cable to the vehicle ground (-). After that, ask the assistant to turn on the starter and read the voltage value. If the voltage is below about 7 volts, the battery must be checked and, if possible, charged before the next attempt to start the engine.
Current measurement
In automobiles, it is relatively rare to need to measure current strength. For example, see section «Spontaneous battery discharge». This requires an ammeter built into the multimeter.
Before measuring the current, the device is adjusted to the measurement range in which the measured current strength is supposed to be. If the current strength is not known in advance, the device is adjusted to the maximum measurement range. If at the same time the device does not show any value, successively switch the device to smaller measuring ranges.
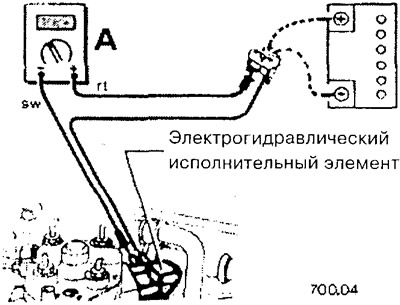
To measure the current, the electrical circuit must be disconnected as shown in the figure, and the measuring device (ammeter) connected to break the circuit. To do this, for example, the plug is disconnected and the red cable (+) ammeter is connected to a current-carrying conductor. Black cable (-) connected to the contact to which the conductor is normally connected. The ground contacts between the power consumer and the plug must be connected with a jumper.
Example: see below section «Spontaneous battery discharge».
Attention: In no case should you measure the current in the wire to the starter with a conventional ammeter (about 150 A) or to diesel engine glow plugs (up to 60 A). The resulting high currents can damage the measuring device. In the workshop, an ammeter with a DC clamp is used for such measurements. In this case, the clamp is connected through an insulated cable, and the current value is measured due to induction.
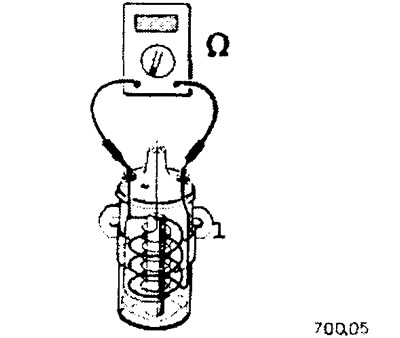
Resistance measurement
Before checking the resistance, it is imperative to make sure that no voltage is applied to the part to which the ohmmeter is connected. That is, you must first always disconnect the plug, turn off the ignition, remove the conductor or assembly, or disconnect the battery. Otherwise, the device may be damaged.
An ohmmeter is connected to two consumer connectors or to two ends of an electrical conductor. It does not matter which cable (+/-) measuring device to which pin is connected.
Measuring resistance in a car can be one of two types:
1. Control of the constant or variable resistance in the electrical circuit.
Example: Check the resistance of the temperature sensor. To do this, disconnect the temperature sensor plug and connect an ohmmeter between the sensor contact and ground (engine block). Set the measuring range of the ohmmeter in which the value of the measured resistance is supposed to lie, and compare the measured resistance with the prescribed value given in the table.
2. Checking the conductivity of an electrical conductor, switch or electric heating element. This checks whether there is a break in the electrical conductor in the vehicle, in connection with which the connected electrical device cannot function. For measurement, an ohmmeter is connected to both ends of the corresponding conductor. If the conductor conducts electricity, then the meter will show a resistance value of 0 ohms. This means that the conductor is in order. If the conductor breaks, the device will show the resistance value» (infinity) Ohm.

Visitor comments