Passat B2 (1981-1988)
Passat B3 (1988-1993)
Passat B4 (1988-1996)
Passat B5 (1996-2005)
Passat B6 (2005-2010)
Car engine repair Volkswagen Passat B3
Basic information about engines
As a power plant in VW PASSAT cars, 4-stroke liquid-cooled engines are used, the axis of rotation of the crankshaft of which in the engine compartment is located perpendicular to...
As a power plant in VW PASSAT cars, 4-stroke liquid-cooled engines are used, the axis of rotation of the crankshaft of which in the engine compartment is located perpendicular to...
The most important characteristics of engines
1) from 8/90: power 66 kW (90 hp) at 5400 1/min; maximum torque 142 Nm at 2600 rpm; ignition and injection system: Mono-Motronic. 2) when using unleaded Super octane gasoline (OC)...
1) from 8/90: power 66 kW (90 hp) at 5400 1/min; maximum torque 142 Nm at 2600 rpm; ignition and injection system: Mono-Motronic. 2) when using unleaded Super octane gasoline (OC)...
Removal and installation of the engine
The engine is removed from the gearbox through the top. Therefore, before removing the engine, you should also read the chapter « Transmission ». The exhaust and intake manifolds,...
The engine is removed from the gearbox through the top. Therefore, before removing the engine, you should also read the chapter « Transmission ». The exhaust and intake manifolds,...
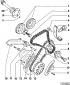
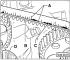
V-belt / toothed belt drive
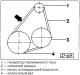
1 — the top casing of a gear belt 2 - bolt, 10 Nm 3 — a protective screen of a gear belt 4 - toothed belt 5 - tension roller 6 - fastening nut, 45 Nm 7 - rear protective screen of...
1 — the top casing of a gear belt 2 - bolt, 10 Nm 3 — a protective screen of a gear belt 4 - toothed belt 5 - tension roller 6 - fastening nut, 45 Nm 7 - rear protective screen of...
Loosening/tensioning of toothed belt
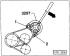
4-cylinder petrol engine Weakening Remove the upper belt guard. Attach a wrench, such as HAZET 2587, to the tension roller. Loosen the tension roller nut with a ring wrench....
4-cylinder petrol engine Weakening Remove the upper belt guard. Attach a wrench, such as HAZET 2587, to the tension roller. Loosen the tension roller nut with a ring wrench....
Removal and installation of a gear belt
4-cylinder petrol engine Removing Up to 9/93: Remove V-belt, see later in this chapter . From 10/93: Remove the V-belt and, if present, the tensioner pulley, see later in this...
4-cylinder petrol engine Removing Up to 9/93: Remove V-belt, see later in this chapter . From 10/93: Remove the V-belt and, if present, the tensioner pulley, see later in this...
Camshaft / valve train 4-cylinder
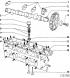
4-cylinder 8-valve engine 1 - bearing cover Pay attention to the offset location of the holes for attaching the cover relative to the bed of the bearing. In a diesel engine, the...
4-cylinder 8-valve engine 1 - bearing cover Pay attention to the offset location of the holes for attaching the cover relative to the bed of the bearing. In a diesel engine, the...
Removal and installation of a camshaft 4-cylinder
4-cylinder 8-valve engine Removing Remove air filter, see chapter « Supply system ». Remove upper toothed belt guard, see above. Remove cylinder head cover 9 Set crankshaft to TDC...
4-cylinder 8-valve engine Removing Remove air filter, see chapter « Supply system ». Remove upper toothed belt guard, see above. Remove cylinder head cover 9 Set crankshaft to TDC...
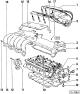
Cylinder head
4-cylinder 8-valve engine 1 - cork 2 - fastening nut, 10 Nm 3 - stiffness bar 4 - cylinder head cover 5 - oil deflector 6 - sealing gaskets of the cylinder head cover 7 — a bolt...
4-cylinder 8-valve engine 1 - cork 2 - fastening nut, 10 Nm 3 - stiffness bar 4 - cylinder head cover 5 - oil deflector 6 - sealing gaskets of the cylinder head cover 7 — a bolt...
Removal and installation of a head of cylinders
Attention: Describes removal for petrol engine. Since, however, not all model variants can be considered, Before removing the cylinder head, it is necessary to check again whether...
Attention: Describes removal for petrol engine. Since, however, not all model variants can be considered, Before removing the cylinder head, it is necessary to check again whether...
Camshaft chain drive 6-cylinder
6 cylinder engine 1 - camshaft sprocket 2 - coupling for the ignition distributor 3 - bolt, 100 Nm 4 - axis, 25 Nm 5 - strap tensioner 6 - tensioner for a double-row roller chain,...
6 cylinder engine 1 - camshaft sprocket 2 - coupling for the ignition distributor 3 - bolt, 100 Nm 4 - axis, 25 Nm 5 - strap tensioner 6 - tensioner for a double-row roller chain,...
Removal and installation of a head of cylinders 6-cylinder
6 cylinder engine 1 - high voltage wire guide 2 - ignition distributor cover with high voltage wires 3 - cylinder head cover 4 — a sealing lining of a cover of a head of cylinders...
6 cylinder engine 1 - high voltage wire guide 2 - ignition distributor cover with high voltage wires 3 - cylinder head cover 4 — a sealing lining of a cover of a head of cylinders...
Checking hydraulic poppets
All engines are equipped with hydraulic poppets. This achieves a reduction in noise and, in addition, there is no need to adjust the clearance in the valve drive as part of the...
All engines are equipped with hydraulic poppets. This achieves a reduction in noise and, in addition, there is no need to adjust the clearance in the valve drive as part of the...
Removal and installation of valves
Removing Remove the cylinder head see above . Caution: If valve drive parts are reused. they must be installed in their original places. To avoid rearrangement of parts in places,...
Removing Remove the cylinder head see above . Caution: If valve drive parts are reused. they must be installed in their original places. To avoid rearrangement of parts in places,...
Replacement valve stem seals
All engines Worn valve stem seals cause high engine oil consumption. The caps are mounted on top of the guides and remove oil from the valve stems. Since the valve springs must be...
All engines Worn valve stem seals cause high engine oil consumption. The caps are mounted on top of the guides and remove oil from the valve stems. Since the valve springs must be...
Checking the valve guides
When repairing engines with leaky valves, it is not enough to just remake or replace the valves. In addition, the valve guides should be checked for wear immediately. The check is...
When repairing engines with leaky valves, it is not enough to just remake or replace the valves. In addition, the valve guides should be checked for wear immediately. The check is...
Seat / valve seat finishing
Does not apply to 16-valve engines Valve seats showing signs of wear or combustion effects may be refinished as long as the maximum allowable refinishing is maintained. If this...
Does not apply to 16-valve engines Valve seats showing signs of wear or combustion effects may be refinished as long as the maximum allowable refinishing is maintained. If this...
Lapping of valve seats
With perfectly machined valve seats and new valves, lapping of the valve seats in the cylinder head is not necessary. Valves may only be lapped using fine-grained grinding paste....
With perfectly machined valve seats and new valves, lapping of the valve seats in the cylinder head is not necessary. Valves may only be lapped using fine-grained grinding paste....
Tensioning / changing the V-belt
Attention: Vehicles manufactured from 8/93 and models with a 1.9 liter supercharged diesel engine with G60 and VR6 engines are equipped with a V-ribbed belt instead of a V-belt to...
Attention: Vehicles manufactured from 8/93 and models with a 1.9 liter supercharged diesel engine with G60 and VR6 engines are equipped with a V-ribbed belt instead of a V-belt to...
Tensioning / replacing the V-ribbed belt
Attention: Vehicles built from 8/93 and models with a 1.9l supercharged diesel engine and with G60 and VR6 engines are equipped with a V-ribbed belt instead of a V-belt. The...
Attention: Vehicles built from 8/93 and models with a 1.9l supercharged diesel engine and with G60 and VR6 engines are equipped with a V-ribbed belt instead of a V-belt. The...
Starting the engine from another car
When starting with an auxiliary jumper cable, pay attention to the following points: The cross-section of the starting cable for petrol engines with a working volume of up to...
When starting with an auxiliary jumper cable, pay attention to the following points: The cross-section of the starting cable for petrol engines with a working volume of up to...
Towing a car
Switch on the ignition to unlock the steering wheel so that the direction indicators, alarm and, if necessary, the windshield wipers can function. Since the brake booster only...
Switch on the ignition to unlock the steering wheel so that the direction indicators, alarm and, if necessary, the windshield wipers can function. Since the brake booster only...
Visual check for oil leaks
If the engine oil consumption is high, oil leaks must be found. To do this, check the following places: Open the filler cap and check the sealing gasket for porosity and damage....
If the engine oil consumption is high, oil leaks must be found. To do this, check the following places: Open the filler cap and check the sealing gasket for porosity and damage....
Checking the V-belt / V-ribbed belt
The condition and tension of the V-belt must be checked as part of the service every 30,000 km. The V-belt must be replaced when: excessive wear fringing of side surfaces traces...
The condition and tension of the V-belt must be checked as part of the service every 30,000 km. The V-belt must be replaced when: excessive wear fringing of side surfaces traces...
Checking the condition and tension of the toothed belt
Checking the toothed belt tension Since incorrectly performed work can lead to significant engine damage, attention must be paid to the precise execution of work operations. The...
Checking the toothed belt tension Since incorrectly performed work can lead to significant engine damage, attention must be paid to the precise execution of work operations. The...
Compression test
1) Except 118 kW motor (160 hp). Compression check allows you to draw a conclusion about the condition of the engine. Namely, it allows you to establish whether the valves or...
1) Except 118 kW motor (160 hp). Compression check allows you to draw a conclusion about the condition of the engine. Namely, it allows you to establish whether the valves or...
Engine Troubleshooting
When the engine does not start, a systematic approach is needed to identify the malfunction. In general, in order for the engine to start, 2 basic prerequisites must always be...
When the engine does not start, a systematic approach is needed to identify the malfunction. In general, in order for the engine to start, 2 basic prerequisites must always be...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections from other manuals for VW cars:
Petrol engines 1.3 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Golf 2 (1984-1993)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.6 and 1.8 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Petrol engine 1.4 CAVA Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Petrol engines 1.4 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Petrol engines 1.3 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Golf 2 (1984-1993)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.6 and 1.8 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Petrol engine 1.4 CAVA Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Transporter T4 (1990-2003)
Petrol engines 1.4 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Passat B6
Passat B5
Passat B4
Passat B3
Passat B2
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Petrol engine 1.6L
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel injection system
- Petrol engine 2.0L
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Fuel and exhaust systems
- Diesel engine 2.0L
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel and exhaust systems
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Mechanical gearbox
- Automatic gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Wheels and tires
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Weekly checks
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Engine management
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Drive shafts
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Wheels and tires
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior (external elements)
- Interior (internal elements)
- Doors and covers
- Ventilation and heating
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Technical data
- 8-valve engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Supply system
- Ignition system
- Fuel injection «Mono-Jetronic»
- Control system «Mono-Motronic»
- Control system «Digifant»
- Control system «Simos»
- 16-valve engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Fuel injection «K-Jetronic»
- Control system «KE-Motronic»
- Control system «Digifant»
- Diesel engine
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Power and control system
- Turbocharging system
- Digital control system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Manual gearbox
- Hydromechanical gearbox
- Front wheel drive
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting and appliances
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Driving Tips
- Maintenance instructions
- Technical data
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Ignition system
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Supply system
- Petrol injection system
- Diesel engine
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Heating system
- Electrical equipment
- Power devices
- Lighting system
- Equipment and devices
- Wiper system
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Introduction to instructions
- User manual
- Power unit
- Engines 4-cylinder FZ
- Engines 4-cylinder
- Engines 5-cylinder
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Four-speed gearbox
- Five-speed gearbox
- Hydromechanical gearbox
- Front wheel drive
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body elements
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Electrical circuits
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •