Digifant injection system, engines with designations ABF, PF, PB, PG, 2E
Caution: Idle speed, CO content and ignition timing must be checked and adjusted together. On engines with a variable catalyst, the oxygen sensor remains connected during the test.
Test prerequisite: The exhaust system must be tight.
Warm up the engine to an engine oil temperature of at least +80°C.
Turn off all electrical consumers, as well as the air conditioning system.
If the fuel lines have been disconnected or replaced, then before checking the engine shaft must be brought to a speed of 3000 1/min several times, and then the engine should be left to idle for at least two minutes.
Attention: Only connect devices with the ignition switched off.
Check ignition timing, see chapter «Ignition system».
Make sure that the crankshaft speed stabilization valve works when the engine is idling. To do this, turn on the ignition and put your hand on the valve. The valve should vibrate and buzz audibly. The valve is located above the cylinder head, next to the throttle valve, see above.
Connect the crankshaft speed meter according to the service manual.
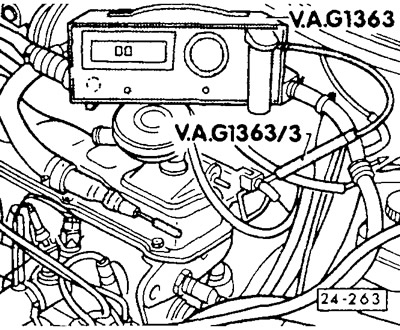
Variable Catalyst Engine (designations ABF, PF, PB, PG, 2E): Connect the CO measuring device to the CO sampling pipe in the engine compartment. The extraction tube is welded to the front exhaust pipe and is usually closed with a light blue cap.
Caution: Push the hose of the measuring device securely onto the sampling tube and make sure that the connection is tight.
112 hp engine (RV designation): Connect the CO measuring instrument to the final outlet pipe.
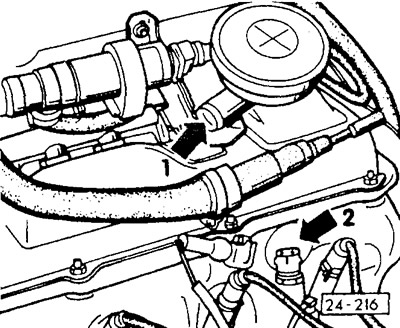
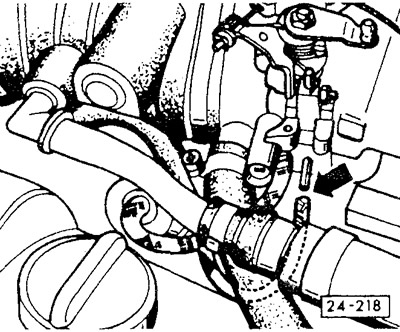
Detach crankcase breather hose at pressure control valve -arrow 1-. Close the hose, for example, with a plug, screwdriver handle or by pinching. Engine designation ABF, 2E: Detach the double hose at the pressure control valve and close only the opening of the hose leading to the intake air hose. If there are two separate crankcase breather hoses, disconnect the breather hose from the intake air hose and seal the hole in the intake air hose with a plug. To do this, you can use the inspection hole cap to set the TDC position, see chapter «Ignition system».
Start the engine and let it idle.
Disconnect the temperature sensor plug after 1 minute (blue) (arrow 2). Engine 2E up to 7/92: after the cooling fan has already been switched on once, disconnect the plug of the coolant temperature sensor with the throttle closed.
Give gas three times while increasing the engine speed to a value of more than about 3000 1 / min. Then leave the engine to idle.
Attention: The fan of the cooling system must not rotate during inspection and adjustment work.
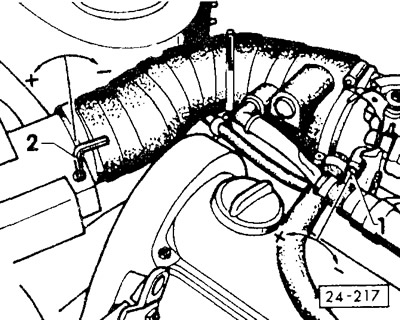
Check engine speed and CO content when idling. If necessary, alternately turn the speed adjusting screw -1- and the CO content adjusting screw -2- to adjust the above parameters to the prescribed values.
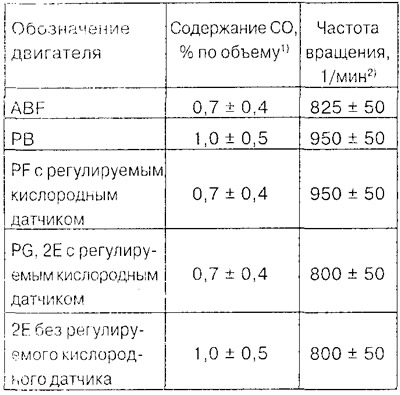
1) The stated CO content is valid up to an altitude of 300 m above sea level. If the place of adjustment is at an altitude of more than 300 m, then for each subsequent 100 m of height, 0.2% by volume must be added. Example: at an altitude of 700 m above sea level, a PB engine should have a CO content of 1.8±0.5% by volume.
2) Temperature sensor plug (blue) disconnected.
Reconnect the blue plug of the temperature sensor and secure.
Give gas three times, then leave the engine to idle.
Check the engine speed and CO content again when idling. The engine speed should now decrease to 800±50 rpm.
Attention: For engines with a controlled catalytic converter, the CO content after connecting the plug of the temperature sensor is regulated independently of the altitude above sea level to a value of 0.7±0.4% by volume.
Engines with catalytic converter (designation PF, PG and 2E up to 7/92)
Checking the regulation of the oxygen sensor. To do this, disconnect the hose from the pressure regulator at the throttle valve connection and close the connecting piece. The CO content should rise for a short time and then fall again. This indicates that the oxygen sensor regulation is OK. If not, check oxygen sensor regulation. Reattach the hose.
Connect the crankcase breather hose to the pressure control valve or to the intake air hose and secure with a clamp.
Attention: If the CO content has now increased, then the reason is not an incorrect adjustment, but an enrichment of the combustible mixture due to the intake of gasoline vapors from the crankcase, where gasoline enters mainly when traveling short distances.
During long continuous trips, the proportion of gasoline in the engine oil decreases, and the CO content in the exhaust gases returns to normal. It can also happen quickly after a 30-minute drive or another oil change.
Switch off measuring devices with the ignition off.
Reconnect all disconnected hoses and wires.

Visitor comments