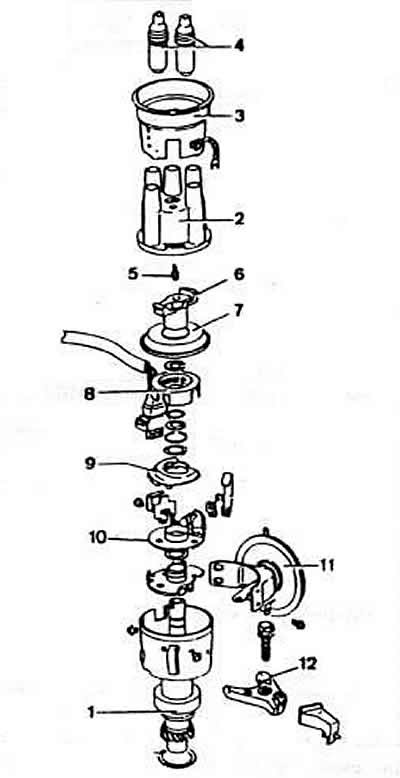
Pic. 2-46. Details of the sensor-distributor of ignition of engines of models «EZ» and «RP»:
1 - housing of the sensor-distributor;
2 - cover of the sensor-distributor;
3 - noise suppression screen;
4 - interference suppression tips of wires;
5 - central electrode;
6 - distributor rotor;
7 - protective screen;
8 - toothed anchor;
9 - wire cover;
10 - Hall sensor;
11 - vacuum regulator;
12 - locking bracket of the sensor-distributor housing.
The characteristics of the automatic ignition advance of the regulators of the engine ignition sensor-distributor are shown in fig. 2-45.
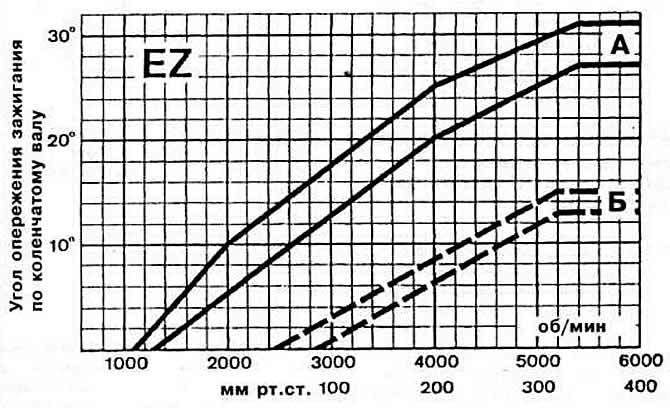
Pic. 2-45. Characteristics of the automatic ignition timing of the regulators of the engine ignition sensor-distributor «EZ»:
A - characteristic of the centrifugal regulator;
B - characteristic of the vacuum regulator. When checking the removed distributor sensor on the stand, divide the values indicated in the graph by two. When checking on the engine, add the value of the initial ignition timing.
Brand and catalog number of the Bosch switch 0 227 100 142.
Device. The ignition system contains a sensor-distributor, an electronic switch and an ignition coil. The distribution sensor has the following main components: proximity sensor, ignition pulse distributor, centrifugal and vacuum ignition timing controllers. During the operation of the ignition timing regulators, the base plate rotates along with the sensor attached to it. When regulating in the direction of ignition advance, the sensor turns in the direction opposite to the direction of rotation of the rotor, and when regulating in the direction of delay, it turns in the opposite direction.
The pulses generated by the sensor control the operation of the switch, which acts as a breaker in the contact ignition system. In addition, the switch provides regulation of the current flow time in the primary circuit of the ignition coil according to a given law as a function of the engine speed and on-board network voltage; limits voltage pulses in the primary circuit of the ignition coil; limits the primary circuit current when it reaches its maximum value; interrupts the primary current when the contacts of the ignition switch are closed and the engine is not running. It also contains a switch protection node from network surges.
Principle of operation.The ignition system uses a non-contact semiconductor sensor. The operation of these sensors is based on the use of the galvanomagnetic Hall effect. This effect is observed in the Hall element, which is a thin plate with four electrodes (pic. 2-47). made of semiconductor material. If a current passes through such a plate in the direction AB and a magnetic field acts on it simultaneously, the direction of action of which H is perpendicular to the plane of the plate, then an emf arises on the faces F and E parallel to the direction of the current. Hall.
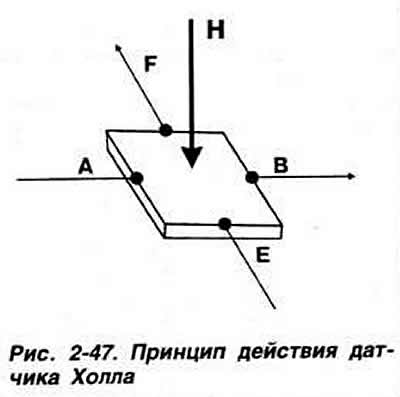
Since the signal from the Hall element is small, it depends on the supply voltage and temperature. semiconductor sensor (Hall Sensor) contains, in addition to the Hall element, a voltage regulator, an amplifier, a temperature compensation circuit, a signal conditioner and an output transistor. All elements are placed in one chip.
In the distribution sensor, the Hall sensor is located at a small distance from the permanent magnet, and a shutter with slots of a given width moves in the gap between them (pic. 2-48). As a result, rectangular pulses are sent from the sensor, which control the operation of the ignition system. Width of the part of the shutter covering the magnetic field «b» corresponds to the angle of the closed state of the breaker contacts. When passing through the slot in the gap, the switch closes the primary circuit of the ignition coil and the primary current flows through it. The interruption of the primary current occurs at the moment of closing the gap, which causes a sharp decrease in current and magnetic flux. The change in magnetic flux ensures the appearance of high voltage in the secondary winding.
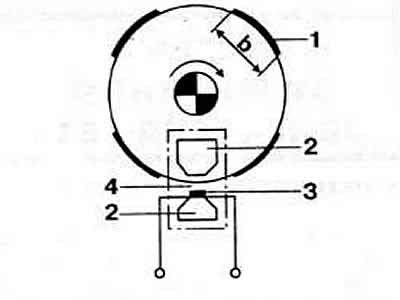
Pic. 2-48. Hall sensor operation scheme:
1 - curtain with slots
2 - permanent magnet
3 - Hall sensor
4 - clearance
In ignition systems with a Hall sensor, the time of energy accumulation in the ignition coil is regulated depending on the engine speed and on-board network voltage. Due to this, the energy of the spark discharge is increased in comparison with other systems by 1.5-2 times and reaches 50 mJ. This ensures the operation of the engine at very lean working mixtures and. as a result, reduced fuel consumption.
Warning. In order not to get injured and not to disable the electronic components of the ignition system, the following rules must be observed.
1. Connect and disconnect the wires of the ignition system only when the power to the ignition system is turned off.
2. Replace the ignition coil only with a coil of the specified type. Do not connect a capacitor to the terminal «1» ignition coils (or switch).
3. If necessary, cranking the crankshaft with a starter without starting the engine (for example, when checking the compression in the cylinders) disconnect the high voltage wire from the central output of the ignition distributor and connect it to a metal part of the engine that has a reliable connection to the negative battery terminal.
4. When starting the engine from an additional power source, its voltage should not exceed 16.5 V, and the connection time should not exceed 1 minute.
5. Wash the car only with the ignition system turned off.
6. When carrying out electric welding work on a car, disconnect the wires from the battery terminals.
7. When towing a vehicle with a faulty ignition system, disconnect the wires from the ignition switch.

Visitor comments