
Pic. 2-50. Structural scheme of STsV «Mono-Jetronic» engine «RP»:
1 - fuel pump;
2 - fuel tank;
3 - fine fuel filter;
4 - fuel pressure regulator;
5 - electromagnetic fuel injector;
6 - ECU;
7 - idle speed regulator;
8 - throttle position sensor;
9 — heater of the inlet pipeline;
10 - coolant temperature sensor;
11 - oxygen content sensor in exhaust gases;
12 - sensor-distributor of ignition with a built-in Hall sensor;
13 - switch;
14 - battery;
15 - ignition switch;
16 - relay for turning on the fuel pump and powering the computer.
The CCS includes an oxygen concentration sensor in the exhaust gases, designed to optimize the composition of the fuel-air mixture. The sensor remains operational when using leaded gasoline and is installed in the exhaust pipe of the mufflers.
The idle speed of the crankshaft and the CO content in the exhaust gases are automatically maintained within the specified limits by the ECU commands and are not subject to adjustment in operation.
As part of the SCV «Mono-Jetronic» includes fuel supply system, air intake system and electrical circuits.
The fuel supply system includes the following elements: a fuel tank, a fuel pump, a coarse fuel strainer, a paper fine fuel filter, a fuel supply and drain line, a nozzle and a fuel pressure regulator.
The fuel tank with a tank capacity of 70 liters is plastic. installed under the body floor behind the rear axle. Bosch brand electric roller fuel pump, catalog number 0 580 453 016, fuel supply pressure 1.2 kgf/cm2 (pic. 2-51) installed in the fuel tank. The pump is switched on and off by means of a relay. When the ignition is turned off and the engine is stopped, the turnip cuts off the power to the pump motor. The fine fuel filter must be replaced every 20,000 km. Nozzle (pic. 2-52) installed in the body of the central injection unit (pic. 2-53) and ensures accurate fuel metering and optimal atomization in the intake manifold. The fuel injection duration of the injector is synchronized in phase with the ignition timing.
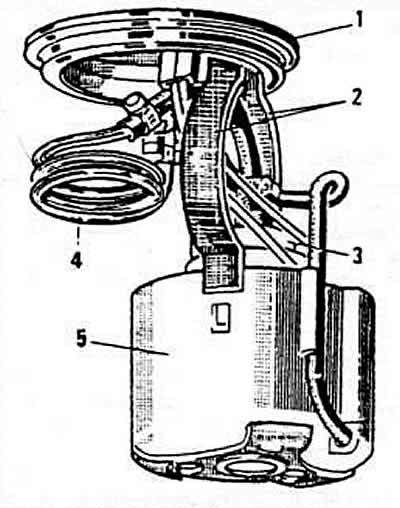
Pic. 2-51. Fuel pump:
1 - pump mounting bracket;
2 - pump clamp;
3 - pump;
4 - damper;
5 - coarse mesh filter.
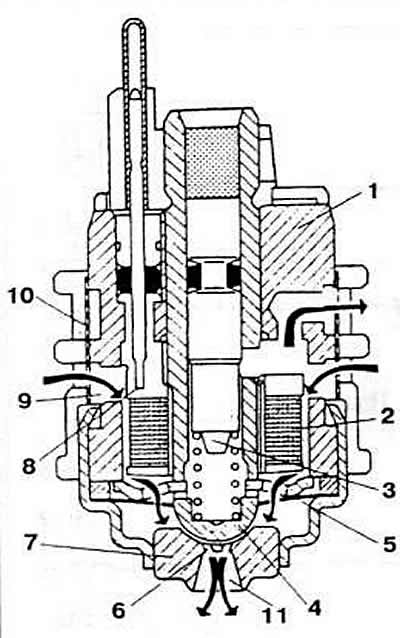
Pic. 2-52. Nozzle section:
1 - body;
2 - winding;
3 - anchor;
4 - shut-off valve;
5 - diaphragm spring;
6 - nozzle hole;
7 - stop valve seat;
8 - electrical connector;
9 - annular fuel supply chamber;
10 - filter;
11 - nozzle.
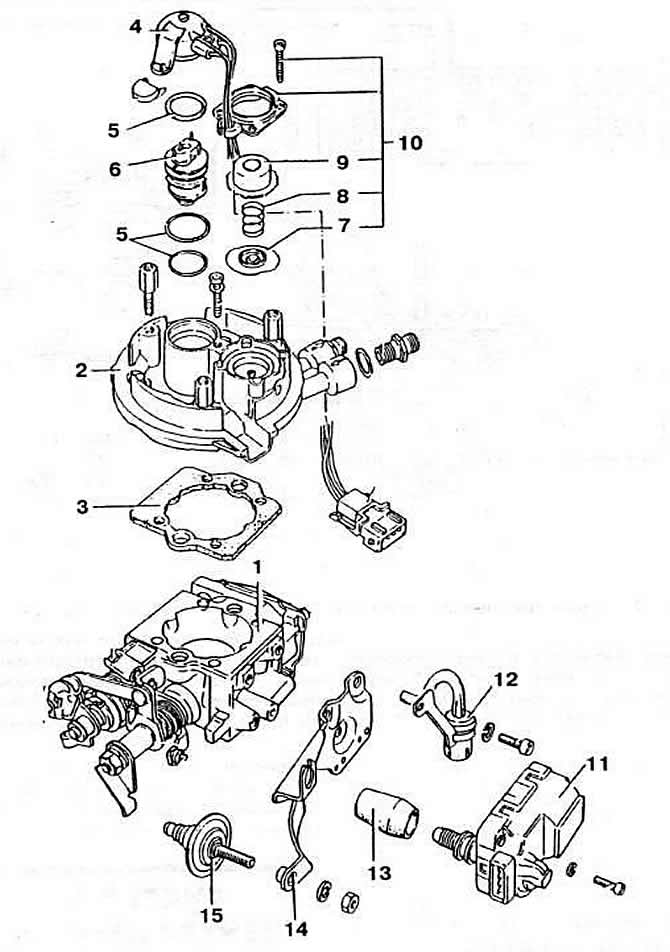
Pic. 2-53. Details of the central injection unit CCV «Mono-Jetronic»:
1 - body;
2 - cover;
3 - sealing gasket;
4 - nozzle holder;
5 - sealing ring;
6 - nozzle;
7 - diaphragm;
8 - spring;
9 - cover;
10 - details of the fuel pressure regulator;
11 - idle speed regulator;
12 - separator;
13 - protective cover;
14 - bracket;
15 - throttle damper.
When forming each signal «Ignition timing» The ECU sends an electrical impulse to the injector winding. Under the influence of the magnetic field created in this case, the shut-off valve is attracted to the armature. The fuel coming through the filter from the annular chamber is sprayed into the inlet pipeline through six nozzle holes in the nozzle seat.
When the flow of electrical impulses from the computer stops, under the influence of the diaphragm spring, the round head of the steam valve sits on the seat, blocking the nozzle holes.
Excess fuel is diverted to the pressure regulator through the top opening of the injector. which ensures that the nozzle is purged, preventing the formation of fuel vapors.
To reduce the voltage at the injector terminals, a ballast resistor is connected in series with it. It is located on the upper support of the right front suspension strut.
Fuel pressure control (pic. 2-54) mechanical, diaphragm type. It is installed in the central injection unit. The fuel drained from the nozzle directly affects the regulator diaphragm, which moves, compressing the return spring under a pressure of 1.06±0.06 kgf / cm2. As a result, the fuel returns to the tank through the cuff.
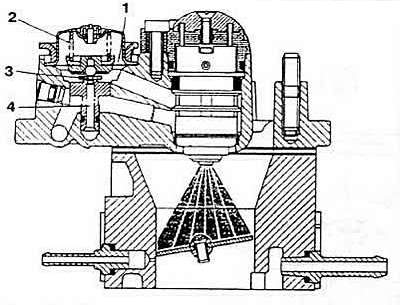
Pic. 2-54. Fuel pressure control:
1 - diaphragm;
2 - compression spring;
3 - cuff;
4 - fuel drain channel.
The air intake system includes an air filter, a central injection unit, a throttle position sensor, an intake air temperature sensor, an idle speed controller, an intake manifold.
Air filter brand Mann, catalog no. 45 152 541 1000 with dry replaceable paper filter element. The filter element must be replaced every 30,000 km.
Bosch brand central injection unit, type C 31152 provides fuel injection, fuel pressure regulation. automatic engine idle control and throttle position detection.
Throttle position sensor potentiometric type. It is mounted on the throttle shaft. The ECU receives two voltage pulses from the sensor. the value of which is proportional to the opening angle of the throttle valve. Signal corresponding to each opening angle. is one of the main parameters. on the basis of which the ECU calculates the main fuel injection time. To prevent sticking of the throttle valve and errors in measuring the opening angle, its axis is mounted on two ball bearings.
The sensor potentiometer slider can move along two conductive tracks. When the throttle opening angle is from 0 to 24g, the signal to the ECU comes from the first track. These positions of the throttle correspond to ten reference points entered into the memory of the ECU. which allows you to track the slightest changes in the angular position of the throttle. As soon as it opens at 18e and up to the full load position, the potentiometer slider simultaneously moves along both tracks. The throttle opening angle range from 18°to the maximum value corresponds to five reference points in the ECU memory. Thus. at a throttle opening angle of 18 to 24°, two voltage pulses are simultaneously supplied to the unit. If the sensor malfunctions, the ECU stops the formation of fuel injector control pulses.
The position of the sensor on the body of the central injection unit is set at the factory and must not be changed in any way during operation. In the event of a sensor failure, both of these assemblies must be replaced.
The intake air temperature sensor is installed in the air intake duct of the central injection unit. The coolant temperature sensor is screwed into the body of the cylinder head. Both sensors have a negative temperature coefficient, i.e. their resistance decreases with increasing temperature. The temperature of the intake air and coolant is transmitted from the sensor to the computer in the form of voltage signals.
idle speed controller (pic. 2-55) is a DC stepper motor that rotates the throttle shaft.
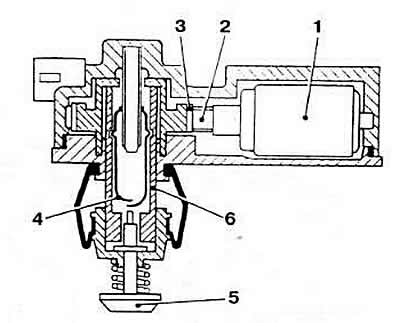
Pic. 2-55. Idle speed controller:
1 - DC stepper motor;
2 - worm;
3 - helical gear;
4 - throttle switch;
5 - stock;
6 - lead screw sleeve.
According to the ECU commands, the regulator turns the throttle when it goes beyond the corner zone, taking into account the tolerance. corresponding to idle speed. Thanks to this, the throttle valve practically remains stationary. thus ensuring stable idling.
A microswitch is built into the regulator, which gives the ECU a signal to close the throttle, on the basis of which the control unit generates a command to stop the fuel supply in the forced idle mode. After the engine speed is reduced to a certain value, and also depending on the temperature of the coolant, fuel injection is resumed at the command of the ECU and the engine switches to idling mode. When the throttle valve is in the idle position with a deviation in one direction or another within the tolerance, the control signal is not supplied to the regulator. When the throttle is out of tolerance, the ECU sends a square wave voltage signal to the governor motor to restore the desired idle speed. If the throttle position continues to change, the controller first receives a continuous signal to quickly return the throttle to the engine idle position, and then a square wave signal to finally adjust the throttle opening. When a control voltage regulator is supplied to the electric motor, a gearbox is activated, consisting of a worm and a helical gear. Inside the wheel there is a lead screw, on which, depending on the direction of rotation of the wheel, the throttle switch housing is screwed or unscrewed. The electrical circuits of the STsV are formed by an ECU with devices connected to it (pic. 2-72) In system «Mono-Jetronic» engine «RP» a double control relay is used to turn on the fuel pump and supply voltage to the computer and injector. It is installed in a box on the left under the instrument panel. The protection circuit breaks the fuel pump supply circuit of the circuit if the ignition is turned on while the engine is not running (for example, in case of an accident).
The ECU is a digital microcomputer, consisting of an analog-to-digital converter, circuits for calculating and controlling input data, and a microprocessor. permanent storage device (ROM) and working memory (RAM). Based on throttle slip and engine RPM information. The ECU uses its own program to calculate the basic duration of the injector valve opening, which determines the amount of fuel entering the engine. 225 values of the basic duration of fuel injection are entered into the memory of the block, which are determined based on 15 throttle positions and 15 steps of the engine crankshaft speed and which correspond to the excess air coefficient a = 1.0 established empirically. In phase with the ignition moment, the basic injection duration can vary within 1-6 ms in order to lean the working mixture in certain engine operating modes, with the exception of starting, engine warm-up and full load mode, as well as at a coolant temperature of less than 75°C and a cold sensor oxygen content in the exhaust gases.
When starting a cold engine, in the event of a decrease in the performance of the fuel pump due to the discharge of the battery, the ECU accordingly increases the duration of fuel injection for an accurate dosage of the fuel-air mixture. During engine warm-up, the degree of enrichment of the combustible mixture is calculated by the ECU depending on the temperature of the coolant, and during acceleration - based on information about the temperature state of the engine, the speed of movement and the initial position of the throttle, and the number of revolutions. The duration of the injection also increases as soon as the throttle valve is opened to an angle of more than 70°, i.e. in full power mode.
If the engine speed exceeds 6200 rpm. generation of injector control pulses and fuel supply is stopped. With the accelerator pedal released, provided. that the throttle switch is depressed, the coolant temperature is above 45°C, and the intake air temperature is above -15°C, the ECU cuts off the fuel supply. If the temperature of the incoming air is in the range from -15°C to +10°C, the fuel supply stops at 2500 rpm and resumes at 2300 rpm, when the air temperature is above 10°C at 1800 and 1300 rpm respectively.
When one or more system devices fail, such as coolant temperature sensors, intake air temperature, oxygen concentration in exhaust gases. throttle position, idle speed controller, the ECU switches to a backup control program, selecting from memory the reference values of the necessary parameters, provided that the ignition system is operating normally. This allows you to continue driving the car, excluding engine failure.
The oxygen concentration sensor measures the oxygen content in the exhaust gases. After processing the signals from the oxygen concentration sensor, the ECU corrects the duration of fuel injection.
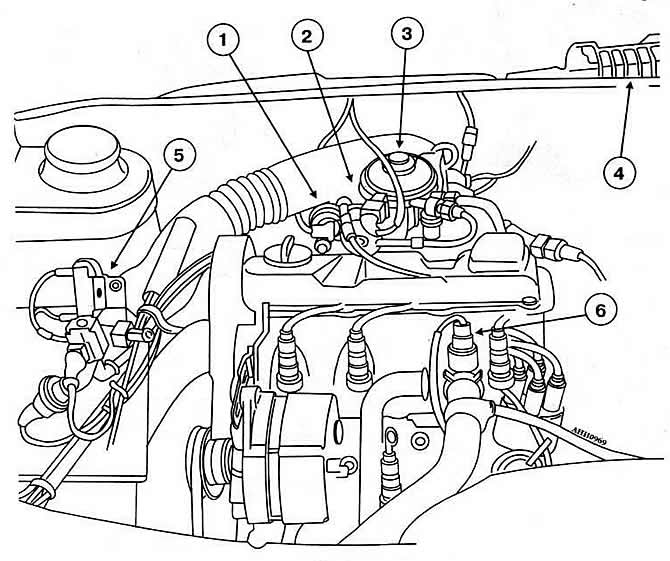
Pic. 2-56. Placement of Mono-Jetronic CCS units in the engine compartment:
1 - idle speed controller
2 - central injection unit
3 - nozzle
4 - ECU
5 - injector ballast resistor
6 - coolant temperature sensor

Visitor comments