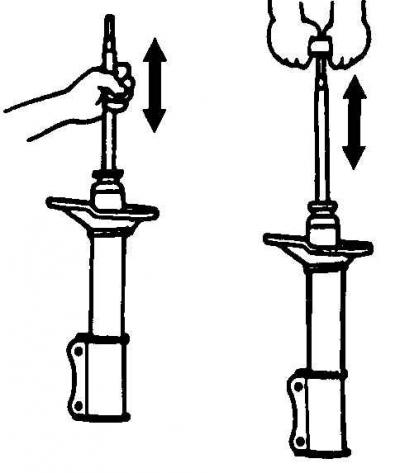
Checking the smooth movement of the shock absorber rod
External manifestations that indicate a malfunction of the shock absorber:
- prolonged rocking of the body when driving on uneven road surfaces;
- increasing body sway when driving on uneven road surfaces;
- uneven and unstable wheel movement (bouncing) when driving in a certain range of speeds, including cornering;
- deviation from the given trajectory of the vehicle during braking;
- unstable cornering and skidding of the car;
- increased tire wear, characterized by abrasion of the tire pattern;
- the appearance of clicks and extraneous noise when the car is moving. Clicks and light bumps can also be the cause of other suspension problems, such as loose threaded connections, failed hub bearings, or worn driveshaft constant velocity joints.
Checking the condition of the shock absorber can be done manually or using special equipment.
To check, remove the shock absorber from the car.
Check the entire length of the damper rod for pitting. Check the shock absorber housing for mechanical damage. Set the shock absorber to a vertical position and check its operation by moving the shock absorber rod through its full stroke. Also check the operation of the shock absorber by moving the shock absorber rod up and down a distance of 50–100 mm. In all cases, the shock absorber rod should move smoothly with perceptible resistance. If the shock absorber rod moves jerkily or there are mechanical damages, the shock absorber must be replaced, see fig. Checking the smooth movement of the shock absorber rod.
With a gas-filled shock absorber, the shock absorber rod can spontaneously extend out of the shock absorber. If there is no spontaneous extension of the rod from the shock absorber, this does not indicate a malfunction of the shock absorber. In this case, the operating mode of the gas-filled shock absorber corresponds to the operating mode of the hydraulic shock absorber. The shock absorber performs its functions without excessive gas pressure, but additional noise may appear when the shock absorber piston moves.
Check the shock absorber for signs of damping fluid leaks. Small oil leaks are allowed while maintaining the normal performance of the shock absorber. If a spot of liquid leaking from the shock absorber reaches only the lower spring seat, then this is considered normahp a slight leakage of fluid from the shock absorber, the sealing ring of the shock absorber rod is also lubricated, which increases its service life.
If there are severe fluid leaks from the shock absorber, the shock absorber must be replaced.

Visitor comments