The cylinder block is made of gray cast iron, in which the engine cylinders are directly made. The cylinder head is made of light alloy and is bolted to the cylinder block. Steel guides and valve seats are pressed into the cylinder head. An oil pan is attached to the bottom of the engine block, into which oil flows, which is necessary for lubricating and cooling the engine.
Gasoline engines use a cross-flow arrangement in which the air-fuel mixture enters the engine cylinders from one side of the engine and the exhaust gases are removed from the other side of the engine. With this engine design, the filling of the cylinders with a fuel-air mixture and the removal of combustion products are significantly improved. On diesel engines, the intake and exhaust manifolds are located on the same side of the cylinder head to save space.
1.6-I petrol engine and 1.9-I diesel engine
The camshaft is mounted in the cylinder head and is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft pulley. The vertically mounted intake and exhaust valves are controlled by camshaft cams via hydraulic tappets. To supply fuel to the cylinders of a diesel engine, a high-pressure fuel pump is used, mounted on the cylinder block and driven by a toothed belt.
Engine 1.8-I
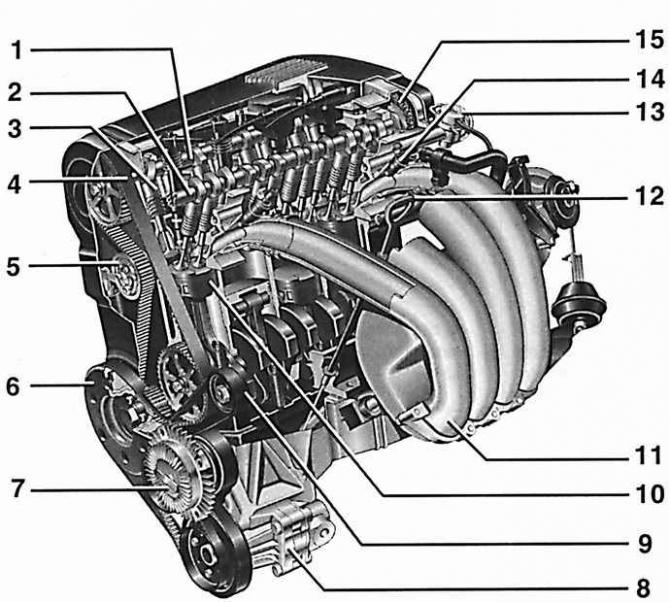
- 1 - camshaft that controls the exhaust valves,
- 2 - camshaft that controls the intake valves,
- 3 - hydraulic pusher,
- 4 - toothed belt,
- 5 - roller of the toothed belt tensioner. Tension roller with pneumatic cushioning,
- 6 - vibration damper,
- 7 - visco clutch hub,
- 8 - power steering pump,
- 9 - generator pulley,
- 10 - piston,
- 11 - pipeline for supplying air to the engine,
- 12 - dipstick for measuring the oil level,
- 13 - fuel pressure regulator,
- 14 - fuel injector,
- 15 - chain
This engine has five valves for each cylinder - 3 intake and 2 exhaust. The valves are driven by two camshafts. One camshaft controls the intake valves and the other camshaft controls the exhaust. The camshaft that controls the exhaust valves is driven by a toothed belt from the crankshaft pulley.
The camshaft that controls the intake valves is driven by a chain from the camshaft that controls the exhaust valves. Increasing the number of valves per cylinder significantly improves the filling of the cylinder with the fuel-air mixture and the removal of combustion products.
Engine 2.3-I (VR5)
In the VR5 engine, five cylinders are located in two planes at an angle of 15°in one cylinder block. Two camshafts mounted in the cylinder head are driven by a chain. Each cylinder has one intake and one exhaust valve.
Engine 2.8-I (6V)
Each cylinder has three intake and two exhaust valves. A separate cylinder head with two camshafts is installed on each section of the cylinder block. One camshaft controls the intake valves and the other the exhaust valves. The camshafts that control the exhaust valves are driven by a single toothed belt. The intake camshafts are driven by the exhaust camshafts.
All engines
Valve clearance adjustment is automatic using hydraulic tappets and no manual adjustment is required.
To supply oil to the rubbing surfaces of the engine, an oil pump is used, which in four- and five-cylinder engines is located in the oil pan and is driven by an intermediate shaft. On six-cylinder engines, the oil pump is located in the front cover of the crankshaft and is driven directly from the crankshaft. Under pressure, oil is supplied to the channels to the bearings of the crankshaft and camshaft.
The water pump on four- and five-cylinder engines is mounted on the side of the engine block. The water pump is driven by a V-belt or V-ribbed auxiliary belt, which also drives the alternator, power steering pump and air conditioning compressor. On a six-cylinder engine, the water pump is located at the front of the engine and is driven by a toothed belt. Keep in mind that engine cooling systems should be filled all year round with a mixture of antifreeze and water with a low lime content.
The preparation and ignition of the fuel-air mixture in the engine cylinders is carried out by the engine control system, which does not require adjustments. The ignition timing and idle speed are controlled by the engine management system. During maintenance, it is necessary to replace the spark plugs and the air filter element.
Warning: The radiator fan may come on after the engine is turned off and the ignition is turned off, so be careful when working on a hot engine. To prevent the radiator fan from turning on, disconnect the electrical connector from the radiator fan motor.

Visitor comments