Diesel engines 1.9L car Volkswagen Polo 3
Specifications for AGP, AQM, AYQ 1.9 D and AGR, ALH 1.9 TD engines
Table 7.1. Engine Specifications Engine code The engine code is located between the gearbox and the engine (pic. 7.1). Additionally, the engine code is pasted on the timing belt...
Table 7.1. Engine Specifications Engine code The engine code is located between the gearbox and the engine (pic. 7.1). Additionally, the engine code is pasted on the timing belt...
Engine disassembly
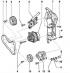
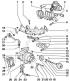
Engine elements are shown in fig. 7.2 a, b. Pic. 7.2 a. Engine elements: 1 - Ribbed belt: 2, 4, 8, 9 - Bolts; 3 - Crankshaft pulley / damper; 5 - Tensioner - ribbed belt (only on...
Engine elements are shown in fig. 7.2 a, b. Pic. 7.2 a. Engine elements: 1 - Ribbed belt: 2, 4, 8, 9 - Bolts; 3 - Crankshaft pulley / damper; 5 - Tensioner - ribbed belt (only on...
Ribbed belt
To remove the ribbed belt: remove the right soundproof casing; mark the direction of movement of the belt; using a wrench, move the tension roller in the direction of the arrow...
To remove the ribbed belt: remove the right soundproof casing; mark the direction of movement of the belt; using a wrench, move the tension roller in the direction of the arrow...
Sealing flange and flywheel
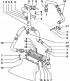
Sealing flange and flywheel are proven in fig. 7.4. Pic. 7.4. Sealing flange and flywheel: 1 - Cylinder block; 2 - Pressure plate / drive plate (only on AGP, AQM, AYQ engines); 3...
Sealing flange and flywheel are proven in fig. 7.4. Pic. 7.4. Sealing flange and flywheel: 1 - Cylinder block; 2 - Pressure plate / drive plate (only on AGP, AQM, AYQ engines); 3...
Connecting rod and piston group
The design features and dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group of engines discussed in this chapter are similar to the design features and dimensions of the connecting...
The design features and dimensions of the connecting rod and piston group of engines discussed in this chapter are similar to the design features and dimensions of the connecting...
Checking piston protrusion at TDC
Piston protrusion at TDC is made when installing a new piston (pic. 7.5). Depending on the protrusion of the piston, the cylinder head gasket is installed (table 7.3). Head Gasket...
Piston protrusion at TDC is made when installing a new piston (pic. 7.5). Depending on the protrusion of the piston, the cylinder head gasket is installed (table 7.3). Head Gasket...
Cylinder head
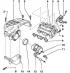
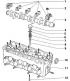
The cylinder head is shown in fig. 7.7. Pic. 7.7. Cylinder head: 1 - Upper part of the timing belt guard; 2 - Toothed timing belt; 3 - Bolt with nut; 4, 5, 10, 12, 21, 28 - Bolts;...
The cylinder head is shown in fig. 7.7. Pic. 7.7. Cylinder head: 1 - Upper part of the timing belt guard; 2 - Toothed timing belt; 3 - Bolt with nut; 4, 5, 10, 12, 21, 28 - Bolts;...
Intake manifold
The intake manifold of AGP, AQM engines is shown in fig. 7.9 a, AYQ engine - in fig. 7.9 b, engines AGR, ALH, ASV - in fig. 7.9 c. Pic. 7.9 a. Intake manifold for AGP, AQM...
The intake manifold of AGP, AQM engines is shown in fig. 7.9 a, AYQ engine - in fig. 7.9 b, engines AGR, ALH, ASV - in fig. 7.9 c. Pic. 7.9 a. Intake manifold for AGP, AQM...
Removing and installing timing belt
Removing On engines AGR, ALH, ASV 1. Disconnect the connection between the compressed air cooler (intercooler) and intake manifold. For all engines 2. Remove the upper part of the...
Removing On engines AGR, ALH, ASV 1. Disconnect the connection between the compressed air cooler (intercooler) and intake manifold. For all engines 2. Remove the upper part of the...
Compression test
On engines AGP, AQM, AYQ 1. Remove the upper part of the intake manifold. For all engines 2. Connect the measuring device to the injection pump (arrow) (pic. 7.19). 3. Remove glow...
On engines AGP, AQM, AYQ 1. Remove the upper part of the intake manifold. For all engines 2. Connect the measuring device to the injection pump (arrow) (pic. 7.19). 3. Remove glow...
Gas distribution mechanism
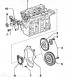
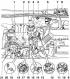
Elements of the gas distribution mechanism are shown in fig. 7.21. Pic. 7.21. Elements of the gas distribution mechanism: 1 - Root covers of the camshaft; 2 - Nut; 3 - Camshaft; 4...
Elements of the gas distribution mechanism are shown in fig. 7.21. Pic. 7.21. Elements of the gas distribution mechanism: 1 - Root covers of the camshaft; 2 - Nut; 3 - Camshaft; 4...
Valve seat processing
1. Insert the valve and press it firmly against the seat. 2. Measure the distance «A» between the end of the valve stem and the top edge of the cylinder head (pic. 7.25). 3....
1. Insert the valve and press it firmly against the seat. 2. Measure the distance «A» between the end of the valve stem and the top edge of the cylinder head (pic. 7.25). 3....
Checking the valve guide
1. Insert the new valve into the sleeve as follows. so that the end of its stem is flush with the edge of the valve sleeve. 2. Determine the gap between the sleeve and the valve...
1. Insert the new valve into the sleeve as follows. so that the end of its stem is flush with the edge of the valve sleeve. 2. Determine the gap between the sleeve and the valve...
Checking hydraulic lifters
Attention! A defective hydraulic compensator must be replaced as a whole. It is beyond repair. Irregular valve knocking when starting the engine is normal. 1. Start the engine and...
Attention! A defective hydraulic compensator must be replaced as a whole. It is beyond repair. Irregular valve knocking when starting the engine is normal. 1. Start the engine and...
Lubrication system
The volume of the lubrication system with oil filter: 4.5 l. The elements of the lubrication system are shown in fig. 7.30 a, b. Pic. 7.30 a.m. Elements of the lubrication system:...
The volume of the lubrication system with oil filter: 4.5 l. The elements of the lubrication system are shown in fig. 7.30 a, b. Pic. 7.30 a.m. Elements of the lubrication system:...
Checking oil pressure and pressure sensor
1. Unscrew the pressure sensor and screw it into the tester (pic. 7.31). 2. Screw the tester adapter into the hole for the pressure sensor in the cylinder head. 3. Connect the...
1. Unscrew the pressure sensor and screw it into the tester (pic. 7.31). 2. Screw the tester adapter into the hole for the pressure sensor in the cylinder head. 3. Connect the...
Cooling system
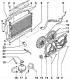
Elements of the cooling system are shown in fig. 7.32 a, b. Pic. 7.32 a. Elements of the cooling system: 1 - Clamp; 2 - Bolts with nuts; 3 - Radiator; 4 - Blocking support; 5 -...
Elements of the cooling system are shown in fig. 7.32 a, b. Pic. 7.32 a. Elements of the cooling system: 1 - Clamp; 2 - Bolts with nuts; 3 - Radiator; 4 - Blocking support; 5 -...
Fuel filter
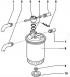
The fuel filter is shown in fig..7.33. Pic. 7.33. Fuel filter: 1 - Drain fuel line (into the fuel tank); 2 - Intake fuel line (from the fuel tank); 3 - Control valve (when...
The fuel filter is shown in fig..7.33. Pic. 7.33. Fuel filter: 1 - Drain fuel line (into the fuel tank); 2 - Intake fuel line (from the fuel tank); 3 - Control valve (when...
Accelerator pedal
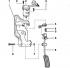
The accelerator pedal is shown in fig. 7.34. Pic. 7.34. Accelerator pedal: 1 - Bracket; 2 - Accelerator pedal position sensor; 3 - Bolt with nut; 4 - Accelerator cable cam; 5 -...
The accelerator pedal is shown in fig. 7.34. Pic. 7.34. Accelerator pedal: 1 - Bracket; 2 - Accelerator pedal position sensor; 3 - Bolt with nut; 4 - Accelerator cable cam; 5 -...
Checking the Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics». The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information:...
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics». The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information:...
Accelerator pedal position sensor adjustment
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics» The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information: 2....
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics» The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information: 2....
Turbocharged diesel engine
The turbocharger with attached elements of the AGR engine is shown in fig. 7.41 a, ALH, ASV engines - in fig. 7.41 b. Pic. 7.41 a. Turbocharger with attached elements of the AGR...
The turbocharger with attached elements of the AGR engine is shown in fig. 7.41 a, ALH, ASV engines - in fig. 7.41 b. Pic. 7.41 a. Turbocharger with attached elements of the AGR...
Intercooler (intercooling of charge air)
Intercooler elements (aftercooling of charge air) shown in fig. 7.42. Pic. 7.42. Intercooler elements (aftercooling of charge air): 1, 10, 12 - Connecting tubes; 2 - O-ring; 3 -...
Intercooler elements (aftercooling of charge air) shown in fig. 7.42. Pic. 7.42. Intercooler elements (aftercooling of charge air): 1, 10, 12 - Connecting tubes; 2 - O-ring; 3 -...
Diesel injection control system
The location of the elements of the diesel fuel injection system in the engine compartment of vehicles with AGP, AQM, AYQ engines is shown in fig. 7.43 a, cars with AGR, ALH, ASV...
The location of the elements of the diesel fuel injection system in the engine compartment of vehicles with AGP, AQM, AYQ engines is shown in fig. 7.43 a, cars with AGR, ALH, ASV...
Self-diagnosis of the injection system
The fuel injection system control unit is equipped with a fault memory that records sensor or system faults, indicating the type of fault. Sometimes there are malfunctions that...
The fuel injection system control unit is equipped with a fault memory that records sensor or system faults, indicating the type of fault. Sometimes there are malfunctions that...
Connecting a fault code reader VAG 1551
1. Remove ashtray 1 and connect fault code reader VAG 1551 with wire VAG 1551/3 (pic. 7.45). 2. After connecting the DTC reader, depending on the selected function, turn on the...
1. Remove ashtray 1 and connect fault code reader VAG 1551 with wire VAG 1551/3 (pic. 7.45). 2. After connecting the DTC reader, depending on the selected function, turn on the...
Fault memory interrogation
To interrogate the fault memory, a VAG 1551 fault code reader and a VAG 1551/3 wire are required. 1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and by typing «01»...
To interrogate the fault memory, a VAG 1551 fault code reader and a VAG 1551/3 wire are required. 1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and by typing «01»...
Clearing the fault memory
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and by typing «01» «Engine electronics», select the engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display...
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and by typing «01» «Engine electronics», select the engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display...
Reading a block of measured values
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics». The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information:...
1. Connect the VAG 1551 fault code reader (V.A.G 1552) and dial «01» «Engine electronics». The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following information:...
Removal and installation of injection pump
Removing 1. Remove the air filter. 2. Remove the top part of the timing belt cover. 3. Remove the cylinder head cover. 4. Disconnect the fuel lines from the injection pump. 5....
Removing 1. Remove the air filter. 2. Remove the top part of the timing belt cover. 3. Remove the cylinder head cover. 4. Disconnect the fuel lines from the injection pump. 5....
Checking the injectors
Injectors are tested on the stand (pic. 7.48). Check the opening pressure while spraying fuel. Engines AGP, AGR, AQM, AYQ Specification value: new nozzle - 190-200 bar,...
Injectors are tested on the stand (pic. 7.48). Check the opening pressure while spraying fuel. Engines AGP, AGR, AQM, AYQ Specification value: new nozzle - 190-200 bar,...
Checking the crankshaft speed sensor
1. Turn off the ignition. 2. Disconnect the wiring connector from the crankshaft speed sensor (pic. 7.49). 3. Measure the resistance between pins 1 and 2 of the connector (pic....
1. Turn off the ignition. 2. Disconnect the wiring connector from the crankshaft speed sensor (pic. 7.49). 3. Measure the resistance between pins 1 and 2 of the connector (pic....
Checking the coolant temperature sensor
1. Connect tester VAG 1551 and dial «01» to select a function «Address word» engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following...
1. Connect tester VAG 1551 and dial «01» to select a function «Address word» engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following...
Checking the fuel temperature sensor
1. Connect the VAG 1551 tester and by typing «01» «Engine electronics», select the engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following...
1. Connect the VAG 1551 tester and by typing «01» «Engine electronics», select the engine control unit. The engine must be running at idle. The display should show the following...
Checking the nozzle needle displacement sensor
1. Turn off the ignition. 2. Disconnect the wiring connector from the injector needle movement sensor (arrow) (pic. 7.59). 3. Measure the resistance between the pins of the...
1. Turn off the ignition. 2. Disconnect the wiring connector from the injector needle movement sensor (arrow) (pic. 7.59). 3. Measure the resistance between the pins of the...
Checking the air mass meter
The flow meter is used by the control unit to determine the amount of injected fuel and control the exhaust gas recirculation. The smaller the signal from the flow meter, the less...
The flow meter is used by the control unit to determine the amount of injected fuel and control the exhaust gas recirculation. The smaller the signal from the flow meter, the less...
Intake manifold changeover valve check
1. Engines AGP, AQM 1. Disconnect the wiring connector (arrow) from intake manifold changeover valve (pic. 7.65). 2. Measure the resistance between the valve contacts (pic. 7.66)....
1. Engines AGP, AQM 1. Disconnect the wiring connector (arrow) from intake manifold changeover valve (pic. 7.65). 2. Measure the resistance between the valve contacts (pic. 7.66)....
Fault codes
For example, on the VAG 1551 code reader, fault code 16502 P0118 035 is determined. The faulty assembly is the coolant temperature sensor. 16502 - Fault code. P0118 - Additional...
For example, on the VAG 1551 code reader, fault code 16502 P0118 035 is determined. The faulty assembly is the coolant temperature sensor. 16502 - Fault code. P0118 - Additional...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Polo 4
Polo 3
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Cooling and lubrication system
- Control system
- Injection system (diesel)
- Supply system
- Exhaust system
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Body
- Interior
- Exterior
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Wiper system
- Lighting system
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Petrol engines 1.4 and 1.6
- Petrol engines 1.4 (V16)
- Petrol engines 1.6 and 1.8
- Diesel engines 1.7 and 1.9
- Diesel engines 1.9 D and TD
- Transmission
- Mechanical gearbox 085
- Mechanical gearbox 020/02K
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and instruments (until 2000)
- Equipment and instruments (after 2000)
- Electrical circuits
- Wiring diagrams (petrol)
- Wiring diagrams (diesel)
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •