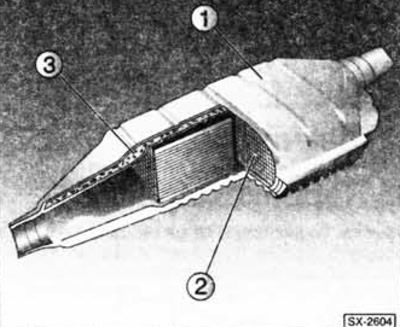
The catalytic converter is designed to clean exhaust gases from harmful products. It consists of a ceramic honeycomb body -2-, which is covered with a carrier layer. On the carrier layer are salts of noble metals, which affect the processes of chemical transformations. In the housing -1-, the catalytic converter is fixed by means of an insulating protective cushion -3-, which, moreover, compensates for thermal expansion.
Connection of electronic petrol injection system and oxygen sensor (sensors) allows you to precisely dose the amount of fuel for combustion so that the catalytic converter can reduce the output of harmful substances. The oxygen sensor is an electrical sensor that indicates the residual oxygen content in the exhaust gases through fluctuations in electrical voltage and allows you to draw conclusions about the composition of the air-fuel mixture.
Since combustion in a diesel engine always occurs with an excess of air, unregulated catalytic converters are used in the exhaust system of these engines. The catalytic converter of a diesel vehicle converts the poisonous carbon monoxide contained in the exhaust gases (SO) and hydrocarbons (SI) respectively into carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (NgO). In addition, it makes it possible to reduce the exhaust opacity typical of a diesel engine.
Higher percentage of nitrogen oxides in diesel engines (NOx) in the exhaust gases is maintained at a low level due to the additional exhaust gas recirculation system (ARF).
Exhaust gas Recirculation valve (ARF valve) located on the inlet pipe and controlled by vacuum. The valve is designed to bypass part of the exhaust gases back into the engine cylinders in order to reduce the combustion temperature and, accordingly, the content of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases.

Visitor comments