Diesel engine coolant hose connection diagram
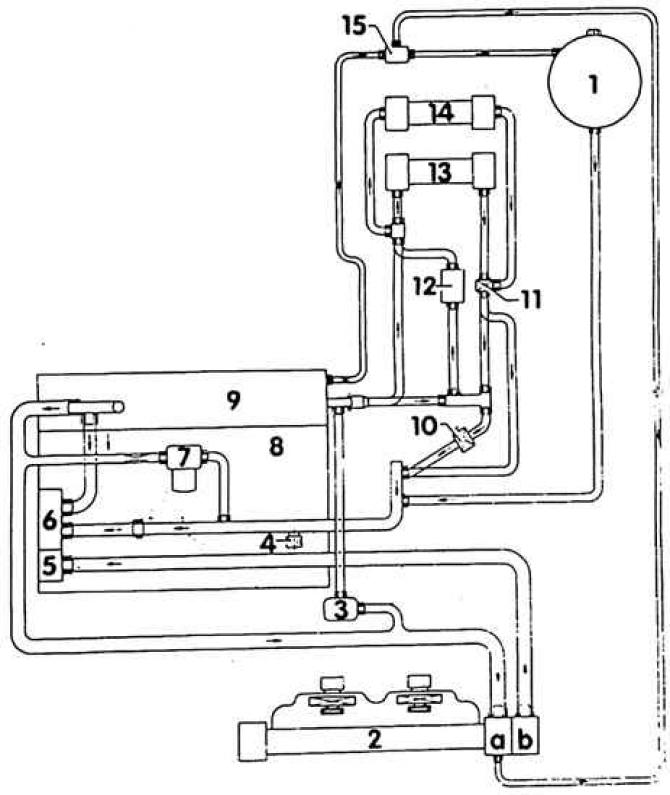
1. Expansion tank; 2. Radiator; A. Up; b. Down; 3. Water circulation pump; 4. Threaded coolant drain plug; 5. Coolant thermostat; 6. Water pump; 7. Oil cooler; 8. Cylinder block; 9. Cylinder head; 10. Magnetic valve. Equipment M; 11. Heating valve; 12. Additional heating. Equipment M; 13. The first heater radiator; 14. Second heater radiator. Equipment M; 15. Tee
Coolant circulation is controlled by a thermostat. While the engine is cold, coolant circulates only in the cylinder head, cylinder block and heat exchanger. As the temperature rises, the coolant thermostat opens a large circulation circuit. The coolant flows through the radiator from top to bottom, while being cooled by the air flow passing between the radiator fins.
To enhance the airflow, the VWT4 has two thermostatically controlled fans. The fans are controlled by a two-stage temperature sensor, which is screwed into the radiator water tank on the right. At a coolant temperature of 84–89°C, the temperature sensor turns on the first stage of the fans (average number of revolutions). If the coolant temperature rises to 90°–95°, the fans will turn on fully.
The 4-cylinder, gasoline engine has an electric fan, the engine of which, through a thin V-belt, drives the second fan. In order for the fan to rotate at medium speed in stage 1, a preliminary resistance is connected. All other engines are equipped with 2 electric fans. Three shutdown relays, which are located on the right, on top of the radiator casing, regulate the speed of rotation of the fans. At the first stage, the fans operate at medium speed and are switched on sequentially. In the second stage, the relay turns on the fans in parallel and at full speed.
Depending on the operating conditions, the optimal operation of the fans is ensured by a protective ring, the plastic plates of which are closed during the engine warm-up phase. This allows the engine to warm up faster. When the engine reaches operating temperature, the plates open automatically, thanks to a thermostat installed behind the radiator, which stretches against the resistance of the springs.
Thanks to the constant operation of the fans, engine power is increased and fuel consumption is reduced.
Attention! Fans can turn on even when the ignition is off. Residual heat in the engine compartment can even cause them to turn on repeatedly.

Visitor comments