Car engine repair VW Transporter T4
Engine device
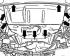
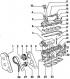
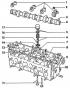
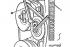
5-cylinder petrol engine 1. Idle stabilization valve; 2. Intake manifold; 3. Dipstick tube for checking the oil level; 4. Exhaust manifold; 5. Oil cooler; 6. Oil filter 7. Oil...
5-cylinder petrol engine 1. Idle stabilization valve; 2. Intake manifold; 3. Dipstick tube for checking the oil level; 4. Exhaust manifold; 5. Oil cooler; 6. Oil filter 7. Oil...
General engine data
Engines on minibuses VW T4 The VW T4 has a transverse engine layout in the engine compartment. Engines are installed 4- and 5-cylinder, both gasoline and diesel. The engines are...
Engines on minibuses VW T4 The VW T4 has a transverse engine layout in the engine compartment. Engines are installed 4- and 5-cylinder, both gasoline and diesel. The engines are...
Removal and installation of the engine
4-cylinder petrol engine The engine is removed downwards without a gearbox. An engine jack or factory machine jack is required to remove the engine. A machine jack and four jack...
4-cylinder petrol engine The engine is removed downwards without a gearbox. An engine jack or factory machine jack is required to remove the engine. A machine jack and four jack...
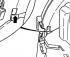
Removing the radiator
1. Unscrew 4 fixing screws (indicated by arrows) on top of the radiator. 2. Pull the radiator by the locking handle (in the middle) first up, then forward. 3. If access to the...
1. Unscrew 4 fixing screws (indicated by arrows) on top of the radiator. 2. Pull the radiator by the locking handle (in the middle) first up, then forward. 3. If access to the...
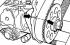
Removal and installation of a mudguard of the engine
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Unscrew combination, hexagon bolts and hexagon nuts (indicated by arrows). 3. Release lock lever. 4. Tilt the mudguard down and remove...
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Unscrew combination, hexagon bolts and hexagon nuts (indicated by arrows). 3. Release lock lever. 4. Tilt the mudguard down and remove...
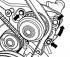
Toothed belt — design description
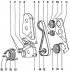
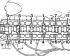
V-belt drive and toothed belt drive of 4-cylinder gasoline engine 1. Bolt, 10 Nm; 2. Lower casing of the toothed belt; 3. Bolt, 20 Nm; 4. Upper casing of the toothed belt; 5....
V-belt drive and toothed belt drive of 4-cylinder gasoline engine 1. Bolt, 10 Nm; 2. Lower casing of the toothed belt; 3. Bolt, 20 Nm; 4. Upper casing of the toothed belt; 5....
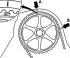
Toothed belt adjustment (petrol 4-cylinder)
Toothed belt tension adjustment Weakening 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Install a nut tool, for example HA2ET 2587, on the tension roller. 3. Loosen the screw securing...
Toothed belt tension adjustment Weakening 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Install a nut tool, for example HA2ET 2587, on the tension roller. 3. Loosen the screw securing...
Toothed belt adjustment (diesel 4-cylinder)
Toothed belt tension adjustment Tension check 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Turn the handle of the VW 210 control device to loosen the spring. 3. Install the tester...
Toothed belt tension adjustment Tension check 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Turn the handle of the VW 210 control device to loosen the spring. 3. Install the tester...
Toothed belt adjustment (petrol 5-cylinder)
Weakening 1. Remove upper toothed belt guard. 2. Loosen the 3 screws securing the water pump. Tilt the shelf to the right with the pry bar and loosen the toothed belt. Tension...
Weakening 1. Remove upper toothed belt guard. 2. Loosen the 3 screws securing the water pump. Tilt the shelf to the right with the pry bar and loosen the toothed belt. Tension...
Toothed belt adjustment (diesel 5-cylinder)
Examination 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and tension eye by one turn. 3. Unscrew the tension eye of the water pump and press the...
Examination 1. Remove upper toothed belt cover. 2. Loosen the alternator mounting bolts and tension eye by one turn. 3. Unscrew the tension eye of the water pump and press the...
Removal and installation of a gear belt (petrol 4-cylinder)
Removing 1. Remove V-belt (see subsection 2.12.1 ). 2. Set the crankshaft to TDC for cylinder 1 and do not change the position again. Installing the engine at TDC for 1 cylinder...
Removing 1. Remove V-belt (see subsection 2.12.1 ). 2. Set the crankshaft to TDC for cylinder 1 and do not change the position again. Installing the engine at TDC for 1 cylinder...
Removal and installation of a gear belt (diesel 4-cylinder)
Adjusting ruler and mandrel for checking the camshaft Usually, the timing is adjusted after a repair in which the toothed belt was removed. If the timing only needs to be checked,...
Adjusting ruler and mandrel for checking the camshaft Usually, the timing is adjusted after a repair in which the toothed belt was removed. If the timing only needs to be checked,...
Removal and installation of a gear belt (petrol 5-cylinder)
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Remove the lower engine compartment cover. 3. Take the car off the stands. 4. Remove V-belt. 5. Set the crankshaft to TDC for the first...
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Remove the lower engine compartment cover. 3. Take the car off the stands. 4. Remove V-belt. 5. Set the crankshaft to TDC for the first...
Removal and installation of a gear belt (diesel 5-cylinder)
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Remove the lower engine compartment cover. 3. Swing the radiator and lock support forward. 4. Remove the alternator and power steering...
Removing 1. Place the machine on stands. 2. Remove the lower engine compartment cover. 3. Swing the radiator and lock support forward. 4. Remove the alternator and power steering...
Cylinder head — design description
Cylinder head of 4-cylinder petrol engine 1. Upper casing of the toothed belt; 2. Mounting bolt, 80 Nm; 3. Camshaft gear; 4. Bolt, 40 Nm; 5. Lower casing of the toothed belt; 6....
Cylinder head of 4-cylinder petrol engine 1. Upper casing of the toothed belt; 2. Mounting bolt, 80 Nm; 3. Camshaft gear; 4. Bolt, 40 Nm; 5. Lower casing of the toothed belt; 6....
Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders (petrol 4-cylinder)
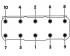
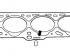
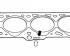
Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Order Cylinder block gasket marks Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders is made on the cold engine. The exhaust manifold is...
Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Order Cylinder block gasket marks Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders is made on the cold engine. The exhaust manifold is...
Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders (diesel 4-cylinder)
Removing 1. Disconnect the wiring from the fuel switch and glow plugs. 2. Clean the supply pipes at the connection points with the pump and nozzles with a cold cleaner and unscrew...
Removing 1. Disconnect the wiring from the fuel switch and glow plugs. 2. Clean the supply pipes at the connection points with the pump and nozzles with a cold cleaner and unscrew...
Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders (petrol 5-cylinder)
Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Order Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold (room temperature). Exhaust and intake manifolds are not removed. The cylinder head can...
Cylinder Head Bolt Tightening Order Remove the cylinder head only when the engine is cold (room temperature). Exhaust and intake manifolds are not removed. The cylinder head can...
Removal and installation of a head of the block of cylinders (diesel 5-cylinder)
Removing 1. Remove the brake booster vacuum hose at the vacuum pump on the side of the cylinder head. 2. Disconnect the coolant hose from the connector on the cylinder head above...
Removing 1. Remove the brake booster vacuum hose at the vacuum pump on the side of the cylinder head. 2. Disconnect the coolant hose from the connector on the cylinder head above...
Removal and installation of the camshaft
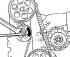
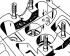
Camshaft and valve drive of a 4-cylinder gasoline engine 1. Main bearing caps; 2. Nut, 20 Nm; 3. Key (working without tightening); 4. Camshaft; 5. Valve cotters; 6. External and...
Camshaft and valve drive of a 4-cylinder gasoline engine 1. Main bearing caps; 2. Nut, 20 Nm; 3. Key (working without tightening); 4. Camshaft; 5. Valve cotters; 6. External and...
Hydraulic Poppet Pushers
All VW T4 engines are equipped with hydraulic poppet lifters, which reduce valve actuation noise and, in addition, do not require valve clearance adjustment as part of...
All VW T4 engines are equipped with hydraulic poppet lifters, which reduce valve actuation noise and, in addition, do not require valve clearance adjustment as part of...
Replacement of oil seals
Spark plug 1. Mass electrode; 2. Ceramic insulator; 3. Central electrode; 4. Glass mass; 5. Connecting pin The reason for the increased oil consumption may be the wear of the...
Spark plug 1. Mass electrode; 2. Ceramic insulator; 3. Central electrode; 4. Glass mass; 5. Connecting pin The reason for the increased oil consumption may be the wear of the...
Removal and installation of valves
Rack for valve drive parts Removing 1. Remove the cylinder head. Attention! If valve drive parts are to be installed again, they must be installed in their original locations. In...
Rack for valve drive parts Removing 1. Remove the cylinder head. Attention! If valve drive parts are to be installed again, they must be installed in their original locations. In...
Checking the valve guides
When carrying out repair work on an engine with leaking valves, it is not enough to treat or replace the valves. Be sure to check the wear of the valve guides. It is especially...
When carrying out repair work on an engine with leaking valves, it is not enough to treat or replace the valves. Be sure to check the wear of the valve guides. It is especially...
Finishing the valve seat in the cylinder head
Valve seats with signs of wear and scorching may be reworked as long as the maximum allowable rework size is maintained. If the rework size is exceeded, the hydraulic valve...
Valve seats with signs of wear and scorching may be reworked as long as the maximum allowable rework size is maintained. If the rework size is exceeded, the hydraulic valve...
Valve seat lapping
With perfectly machined valve seat rings and new valves, lapping of the valve seats in the cylinder head is not required. 1. Valves may only be lapped with fine-grained grinding...
With perfectly machined valve seat rings and new valves, lapping of the valve seats in the cylinder head is not required. 1. Valves may only be lapped with fine-grained grinding...
Cylinder compression check
Compression check allows you to make a conclusion about the condition of the engine. Based on the results of the check, the degree of wear of valves or pistons can be established...
Compression check allows you to make a conclusion about the condition of the engine. Based on the results of the check, the degree of wear of valves or pistons can be established...
V-belt alternator or alternator and water pump
Attention! Depending on the equipment and in order to facilitate access, it is sometimes necessary to tilt the radiator forward (see subsection 2.2 ). Replacement and tension 1....
Attention! Depending on the equipment and in order to facilitate access, it is sometimes necessary to tilt the radiator forward (see subsection 2.2 ). Replacement and tension 1....
Power Steering Pump V-Belt
The V-belt is correctly tensioned if, when pressed with the thumb between the two belt pulleys, it flexes by about 5 mm. The V-belt is tensioned by adding or removing spacers...
The V-belt is correctly tensioned if, when pressed with the thumb between the two belt pulleys, it flexes by about 5 mm. The V-belt is tensioned by adding or removing spacers...
Removal, installation and tension of the wedge toothed belt
Since September 1992, some 4-cylinder engines have been fitted with toothed V-belts instead of V-belts. Checking and adjusting the timing V-belts is not required, as the...
Since September 1992, some 4-cylinder engines have been fitted with toothed V-belts instead of V-belts. Checking and adjusting the timing V-belts is not required, as the...
Engine Troubleshooting
If the engine does not start, you should look for the cause, systematically narrowing the search circle. For an engine to start at all, two basic conditions must be met. The...
If the engine does not start, you should look for the cause, systematically narrowing the search circle. For an engine to start at all, two basic conditions must be met. The...
This section is available on russian, bulgarian, belarusian, ukrainian, serbian, croatian, romanian, polish, slovak, hungarian
Similar sections from other manuals for VW cars:
8-valve engine: Engine repair Volkswagen Passat B4 (1988-1996)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Golf 2 (1984-1993, petrol)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.4 and 1.6 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Engine 2.0 (petrol) Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Petrol engines 1.6 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
8-valve engine: Engine repair Volkswagen Passat B4 (1988-1996)
Power unit: Engine repair Volkswagen Golf 2 (1984-1993, petrol)
Power unit: Petrol engines 1.4 and 1.6 Volkswagen Polo 3 (1995-2003)
Power unit: Petrol engine 4.2L Volkswagen Touareg 1 (2002-2006)
Power unit: Engine 2.0 (petrol) Volkswagen Tiguan 1 (2007-2015)
Petrol engines 1.6 l: Engine repair Volkswagen Caddy 3 (2003-2010)
Transporter T4
Transporter T3
- General information
- User manual
- Maintenance
- Power unit
- Engine repair
- Ignition system
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Fuel system (petrol)
- Fuel system (diesel)
- Injection system (petrol)
- Exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Car suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Body
- Exterior
- Interior
- Doors and windows
- Heating system
- Electrical equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Lighting and signaling
- Power devices
- Electrical circuits
- General information
- Maintenance
- Petrol engines
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and exhaust system
- Carburetor 34 PICT
- Carburetors 2E3 and 2E4
- Fuel injection system
- Ignition system
- Diesel engines
- Engine repair
- Lubrication system
- Cooling system
- Power and exhaust system
- Transmission
- Clutch
- Car gearbox
- Chassis
- Front suspension
- Rear suspension
- Steering
- Brake system
- Body
- Body and interior elements
- Doors, locks and windows
- Electrical equipment
- Lighting system
- Equipment and devices
- Power devices (diesel)
- Power devices (petrol)
- Wiring diagrams (diesel)
- Wiring diagrams (petrol)
VWmanual.ru © 2016-2024 | Mobile version | News and articles | Sitemap: EN BG BY UA RS HR RO PL SK HU | Write message | Site search
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •
Passat B2 • Passat B3 • Passat B4 • Passat B5 • Passat B6 • Golf 1, diesel • Golf 1, petrol • Golf 2, petrol • Golf 2 • Golf 3 • Golf 4 • Golf 5 • Polo 3 • Polo 4 • Touareg 1 • Tiguan 1 • Sharan 1 • Transporter T3 • Transporter T4 • Beetle • Caddy 3 •