Diesel engine power system
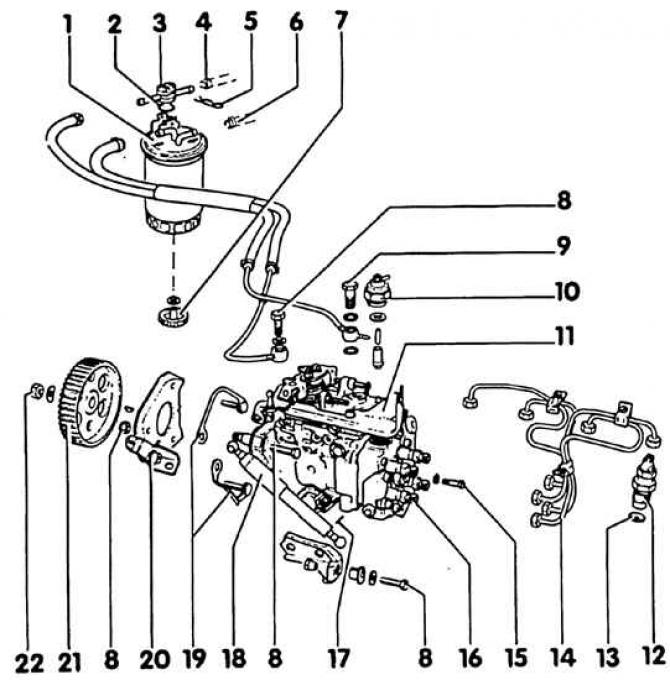
1. Fuel filter - do not mix up the connections. The direction of the section is marked with arrows; 2. Ring; 3. Regulating valve; 4. Fuel return line (to the fuel tank); 5. Locking bracket; 6. Fuel supply pipe (from fuel tank); 7. Water drain screw; 8. Bolt, 25 Nm; 9. Hollow screw, 25 Nm - Hollow screw of the fuel return pipe is marked "OOT"; 10. Traction switch, 40 Nm; 11. High pressure fuel pump (injection pump); 12. Nozzle, 70 Nm; 13. Heat insulator; 14. Piping, 25 Nm; 15. Bolt, 15 Nm - in case of depressurization, tighten with a torque of no more than 25 Nm; 16. Connecting pipe; 17. Retainer; 18. Shock absorber; 19. Holder; 20. Console; 21. High pressure fuel pump gear; 22. Nut, 45 Nm
In a diesel engine, clean air is sucked into the cylinders when the piston moves down and is compressed sharply. In this case, the temperature in the cylinders rises above the ignition temperature of diesel fuel. If the piston is in front of the TDC, then diesel fuel is injected into the heated to a temperature of 700-900°C, which ignites spontaneously, so no spark plugs are required.
When the engine is cold, the ignition temperature cannot be reached by compression alone. In this case, it is necessary to warm up the engine. To do this, a glow plug is located in the swirl chamber, which heats the combustion chamber. The glow time control unit supplies the glow plugs with current both during and after the engine is started. In addition, the diesel engine has a cold start accelerator, which is controlled by a throttle, the button of which is located on the instrument panel, before starting. Cold start accelerator pulling out high pressure fuel pump distributor plunger (injection pump) shifts about 2.5°earlier. At the same time, fuel is also injected into hot air earlier and a cold engine starts faster. As soon as the engine reaches operating temperature, the cold start accelerator cable must be returned to its original position by sinking the button on the instrument panel to the end.
Fuel injection pump is taken directly from the fuel tank. In the injection pump, the fuel, before injection, is compressed to 130-160 bar, then it is fed into the engine cylinders in the order of their operation. At the same time, the injection pump regulator measures fuel depending on the position of the gas pedal. Through the nozzles, diesel fuel is injected at a certain point in time into the prechamber of the corresponding cylinder. Due to the shape of the prechamber or swirl chamber, the incoming air receives a certain swirl during compression, in which the fuel is optimally mixed with the air.
Before the fuel enters the injection pump, it passes through the fuel filter, where it is cleaned of contaminants and water. Therefore, it is very important to clean or replace the filter in a timely manner, according to the prescribed maintenance.
HPF does not require maintenance. All moving parts of the pump are lubricated with diesel fuel. High pressure fuel pump - driven from the crankshaft by a toothed belt.
Since the diesel engine is a self-ignition engine that does not require a distributor ignition system, it has a solenoid valve. When the ignition is turned off, the voltage supply to the solenoid valve is interrupted and the valve closes the fuel channel. This ensures that the fuel supply is cut off before the steering lock closes. When the engine is started, voltage is applied to the solenoid valve, when the starter is turned on, and it opens the fuel channel.

Visitor comments